Pfizer Process 2 Endotoxin Myocarditis Death Toll - Dr Aseem Malhotra knows all about it
Jab your Children and Death from Myocarditis is an expected outcome
Jab pushers are outraged at the overwhelming success of the Australian lecture tour by British Cardiologist Dr Aseem Malhotra.
So let’s look at Jab Deaths caused by the Heart condition known as Myocarditis.
139 Medically Confirmed Myocarditis Deaths
That is just the summary of the 27 pages of discussion of the tragedy discussed by the European Medicines Agency covering cases only to June 2022.1
Imagine how many more have suffered in the year since!
I am circulating this article to inform some journalists and politicians of the facts.
Then I will add details that would take it beyond the Substack email distribution length for those interested in the wealth of detail, including individual Autopsy cases.
PSUR3 Update to 18 Jun 2022
In an Appendix to PSUR 3 we see that Pfizer officially describes all 10,363 cases of Myocarditis to 18 June 2022 as SERIOUS.
We see, without discussion on the right hand columns the data for the Non-Interventional C4591009 study using the worldwide resources of Pfizer.
New Myocarditis cases reported at the rate of 2,312 per month for Jabbees versus 7 per month for the Unjabbed.
Mechanisms are known
As I briefly discussed with Dr Malhotra in Melbourne on 31 May 2023, the mechanisms of Heart Damage by the Process 2 mRNA are multiple and known.
Endothelial Damage will lead to Sudden Death.
"Two-Hit" Shwartzman Anaphylaxis after mRNA jabs explained
In a recent post I reported that Endotoxin in mRNA jabs can float free outside the Lipid Nanoparticles (LNP) as well as adhering to the surface or trapped inside. It remains to be seen how much Endotoxin is bound to mRNA or contaminant DNA or “bioburden”.
Atrial Fibrillation Kills
Atrial Fibrillation is the most common type of Tachycardia, Anaphylaxis leading to Sudden Death caused by Endotoxin in mRNA Jabs
In recent articles I covered Heart Damage and Deaths arising from Positive Feedback Loop generation of damaging microRNAs, and Anaphylaxis Deaths, all caused by Endotoxin that arises from the use of E coli bacteria in production. Direct Endotoxin damage to the Heart and its blood supply system cells from Inflammatory Interleukins is well known.
Myocarditis is an Autoimmune disease caused by the Jabs
Autoimmune Diseases caused by Endotoxin in mRNA Jabs include Myocarditis, Pericarditis Lupus
Recently I briefly mentioned that Endotoxin, as found in every vial of Moderna and Pfizer jab, causes Autoimmune Diseases. While mRNA in the jabs undoubtedly was designed to make Spike Protein invade your cells so they become targets for Destruction, with the announced lie that would be confined to your Muscle Cells, we need to look in more detail at th…
It is known why Young people suffer more Myocarditis
Endotoxin in Pfizer Jabs causes Heart Damage
As I have recently stressed, every vial of Pfizer jab contains Endotoxin arising from the manufacturing process. The jabs are known to cause Heart Damage, evident from the initial trial.Geoff Pain PhD is a reader-supported publication. To receive new posts and support my work, consider becoming a free or paid subscriber.
Rapid Onset of Myocarditis
9.4% of Pfizer induced Myocarditis victims suffered in <24 hours and a further 49.8% from 1 to 5 days. That is before the body had time to make antigens to synthetic Spike coded by the mRNA.
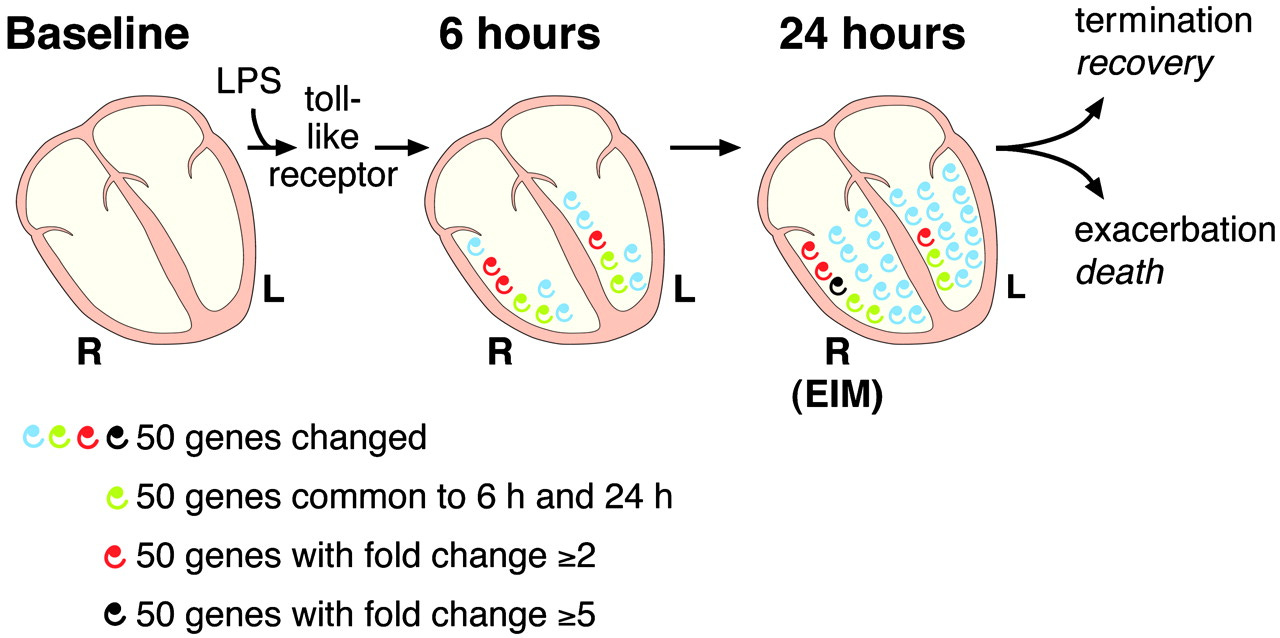
EIM - Endotoxin Induced Myocarditis 2003
I am constantly discovering acronyms. Latest was created by Wong et al. in 2003 as the result of animal studies where Myocarditis was deliberately caused by jabbing rats to cause Systemic Response Inflammatory Syndrome (SIRS).2
By elegant gene analysis, it was found that the Right Ventricle suffers more damage than the Left. Their Figure 3 shows genes that demonstrated fold change 5 or higher at 24 h after a single Endotoxin injection.
This experiment showed the injected Endotoxin effectively bypasses the Liver and travels to numerous organs via the Lymphatic system, as planned by the Pfizer/BioNTech Covid19 jabs.
The Epigenetic changes induced by Endotoxin are well known.
Epigenetics of Endotoxin Poisoning from Pfizer Jabs
In earlier articles I discussed the use of Escherichia coli Bacteria in production of the Pfizer jabs and how supertoxic Endotoxins carry through to the vials. Pfizer is legally obliged to measure and report the Endotoxin levels in the jabs but so far has redacted all documents that include actual measured levels using the Horseshoe Crab Blood test.
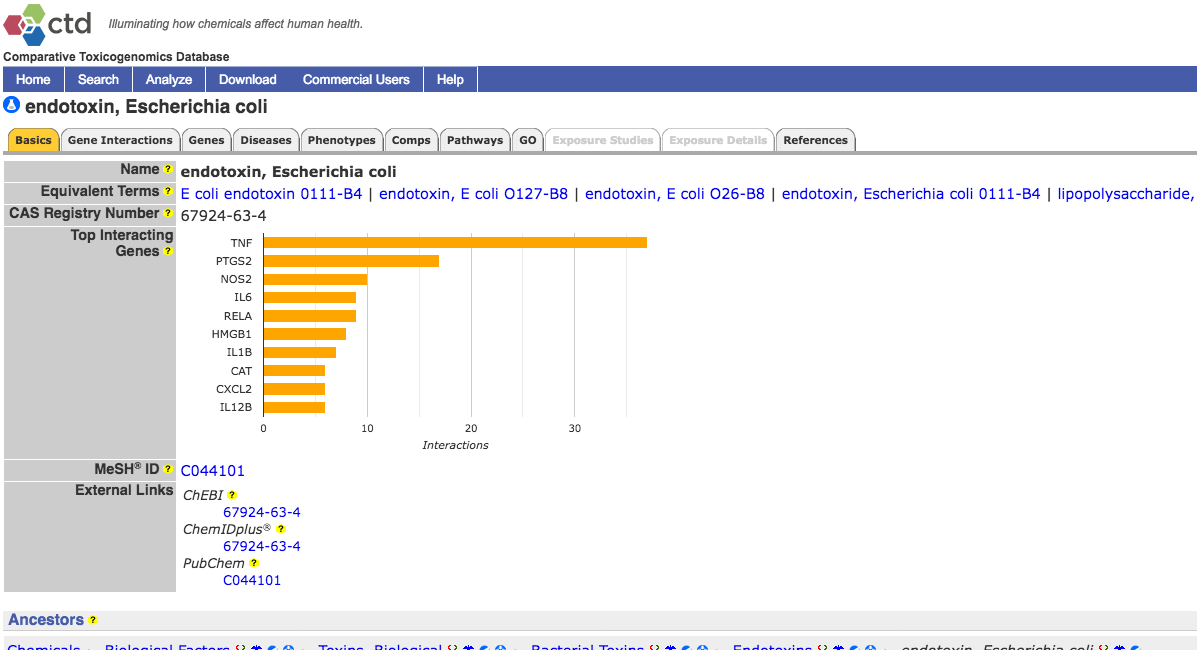
CTD references to Endotoxin Induced Myocarditis
As mentioned earlier, the US government Comparative Toxicogenomics Database is a huge resource. Here is a snippet that it displays for references to the science of EIM.
From that page, each reference can be expanded to see the abstract and link to the original papers.
Calpain is mentioned.3
Drug treatment with Leonurine.4
Protective role of Cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.5
Diagnosis of Clozapine induced Myocarditis from The Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.6 Behind a paywall, so I will have a close look at this later.
Tumor Necrosis Factor ligand superfamily expression in EIM patients.7
Not listed on the page of the CTD for E coli 055-B5 shown above, is another paper looking at treatment of EIM with Metformin.8 Liu and coworkers found that treatment with metformin inhibited the cardiac expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) in endotoxin-challenged mice and suppressed the upregulation of myeloperoxidase (MPO), decreased the elevation of creatinine kinase-myocardial band (CK-MB) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP).
Some original reports of jab induced Myocarditis
Briefly listing the work of research groups in England9, Germany101112, USA13, Japan1415 and Switzerland.16
CD68 Macrophages are caused by Endotoxin
A number of these Myocarditis studies found elevated CD3, CD4 and CD68 cells (histiocytes) in the heart biopsies.17 Choi and coworkers in Korea found CD68 cells in the Heart of a 22-year-old man.18
Nushida and coworkers19 used staining to show the multiple organs including the Heart were damaged by a 3rd Pfizer jab, with a 14-year-old girl dying 2 days after her jab.
In Germany a 76-year-old man with Parkinson’s disease had a jab of AstraZeneca as his first Covid19 insult and suffered mental deterioration after his first Pfizer and again after his second Pfizer jab. He suffered Myocarditis and Multifocal Necrotizing Encephalitis. Autopsy found CD68 cells in his Brain.20
Another man in Germany died just 2 days after his Pfizer jab. He had lots of CD68 and hardly any Spike, as expected due to Endotoxin working its deadly magic faster than any other component of the jabs.21
End stage Kidney Failure patients also exhibit increased expression of CD68 cells in multiple organs.22
CD68 cell development is directly related to Endotoxin cytokines TNF-α and IL-6.23
Myocardial Na/K-ATPase activity is inhibited during endotoxemia via PI3K/Rac1/NADPH oxidase activation. Inhibition of Na/K-ATPase activates Ca2+/CaMK/mTOR signaling, which promotes myocardial TNF-α protein production and cardiac dysfunction during endotoxemia.24
Small Calcium-regulating proteins S100A8 and S100A9
In 2008 Boyd and coworkers studies Endotoxin Induced Myocarditis in detail using HL-1 cells which are from an immortalized cell line with adult cardiac morphological, biochemical, and electrophysiological properties, including contraction and biochemical response to cognate ligands.25
They discovered that 2 small Calcium-regulating proteins (S100A8 and S100A9) are highly upregulated by Endotoxin. They are found in both the intracellular and extracellular spaces. Upregulation of these proteins leads to signaling via RAGE (Receptor for Advanced Glycation End products) to induce chemotaxis of neutrophils and amplification of the proinflammatory cascade, causing decreased contractility.
Boyd et al. also studied the impact of Endotoxin in murine ventricular myocytes, isolated from 10- to 14-week-old adult male mice.
Their paper includes numerous useful references to prior work on Endotoxin Heart Damage.
Galectin 3 enhances Endotoxin Myocarditis
Galectin 3 is used as a measure of Heart damage including Myocarditis scar tissue.
Galectin 3 however is also part of the autoimmune inflammatory process in conjunction with Endotoxin, as reviewed by Srejovic and Lukic.26
“Initial necrosis of cardiomyocytes facilitates Galectin-3–TLR-4 interaction and activates proapoptotic pathways in healthy myocardial cells directly or by Th1 pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the absence of Galectin-3 Th2 cells prevailed and cardiomyocyte cell damage is mediated by IL-4.[70]”
Reference [70] cited above was the work of Zhang and coworkers.27
Researchers in Taiwan showed in 2021 that Galectin-3 promotes inflammasome activation through intracellular binding to Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) glycans.28 This results in amplification of Endotoxin-induced caspase-4/11 oligomerization and activation, causing more intense pyroptosis.
Pyroptosis caused by Endotoxin (LPS) is nicely illustrated by Zheng and coworkers.29
Pyroptosis (“pyro” Greek for fire and “ptosis,” falling) is a highly inflammatory mode of regulated cell death which has evolved as a way of removing intracellular pathogens and has a distinct morphology which depends on the formation of plasma membrane pores resulting in cell explosion.30
Galectin and Endotoxin damage numerous Organs
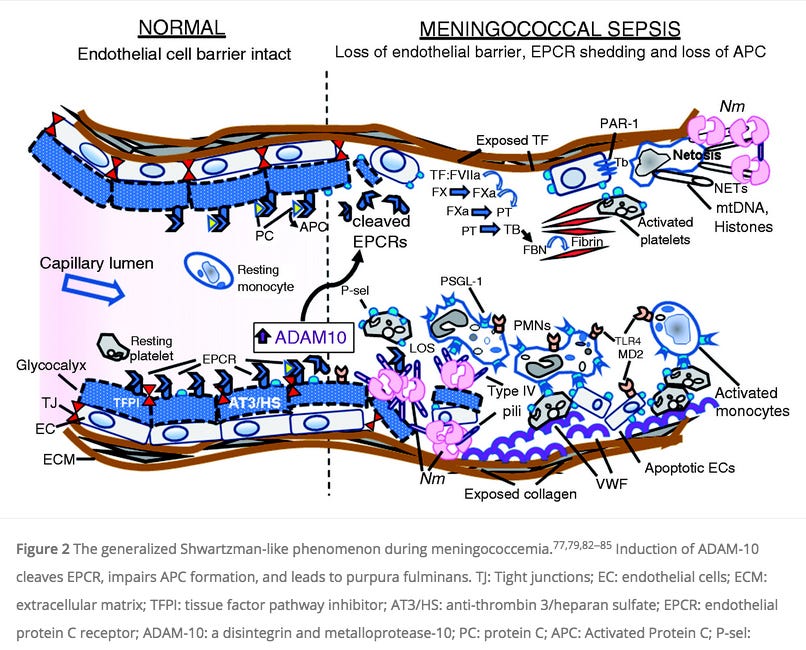
As mentioned above, numerous organs will be simultaneously damaged by mRNA jab induced Sepsis as shown on this scheme by Bouffette and coworkers.31
Damaged Heart cells secrete HMGB1
High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is an alarmin that has been implicated in both Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction and the Lethality associated with Sepsis Endotoxemia.32
August 2023 Update
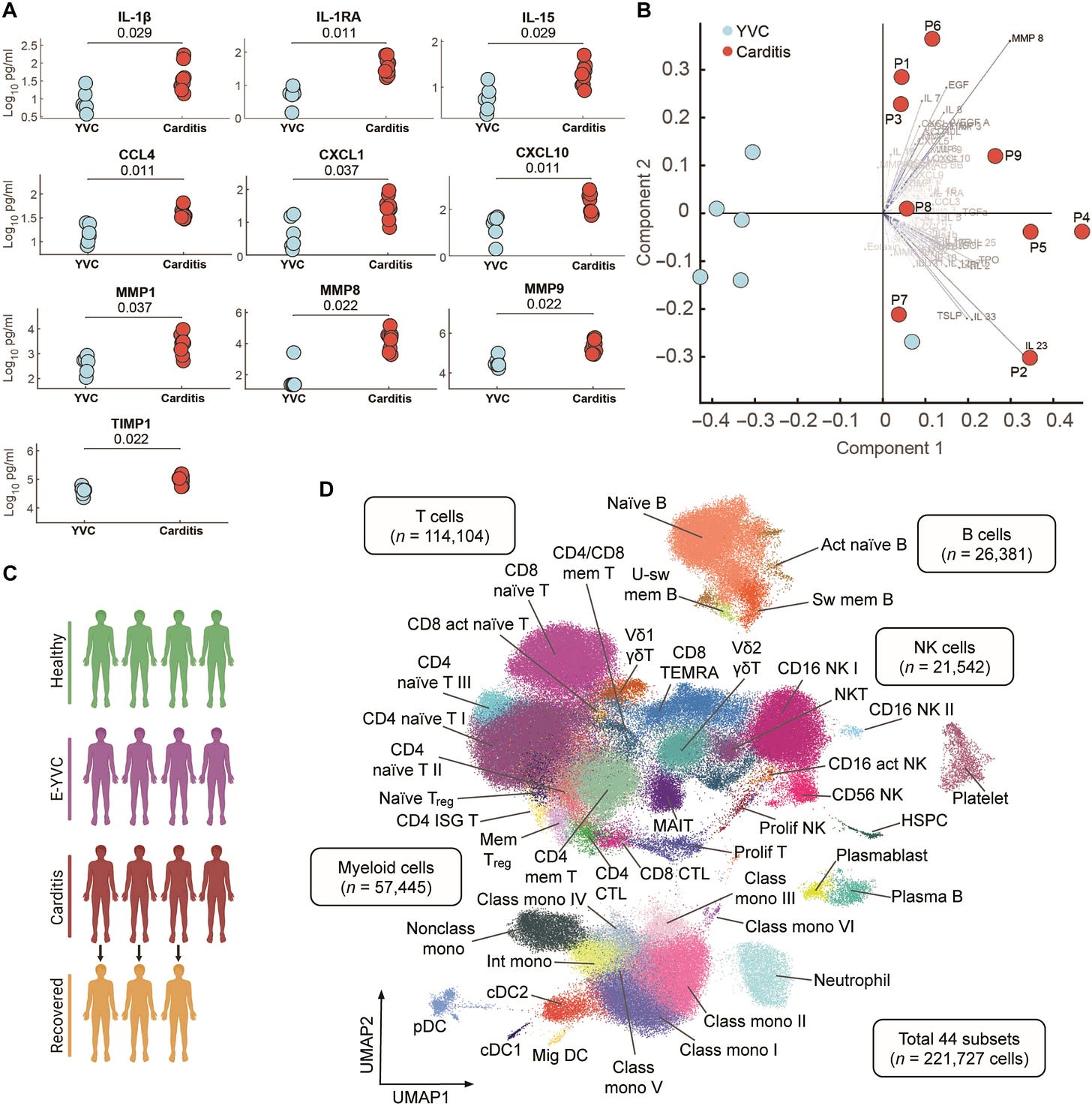
Thanks to Josh Guetzkow reminder, a recent paper that will be mentioned in my book chapter commissioned by AMPS, confirms Cytokine Storm as the basis of Myocarditis.33 These researchers found No evidence of cardiac-targeted autoantibodies. They did find elevations in circulating interleukins (IL-1β, IL-1RA, and IL-15), chemokines (CCL4, CXCL1, and CXCL10), and matrix metalloproteases (MMP1, MMP8, MMP9, and TIMP1), all consistent with Endotoxin epigenetics discussed in my Substack of 13 February 2023 (link above).
Update on Endotoxin Cardiac Death via Aldose Reductase
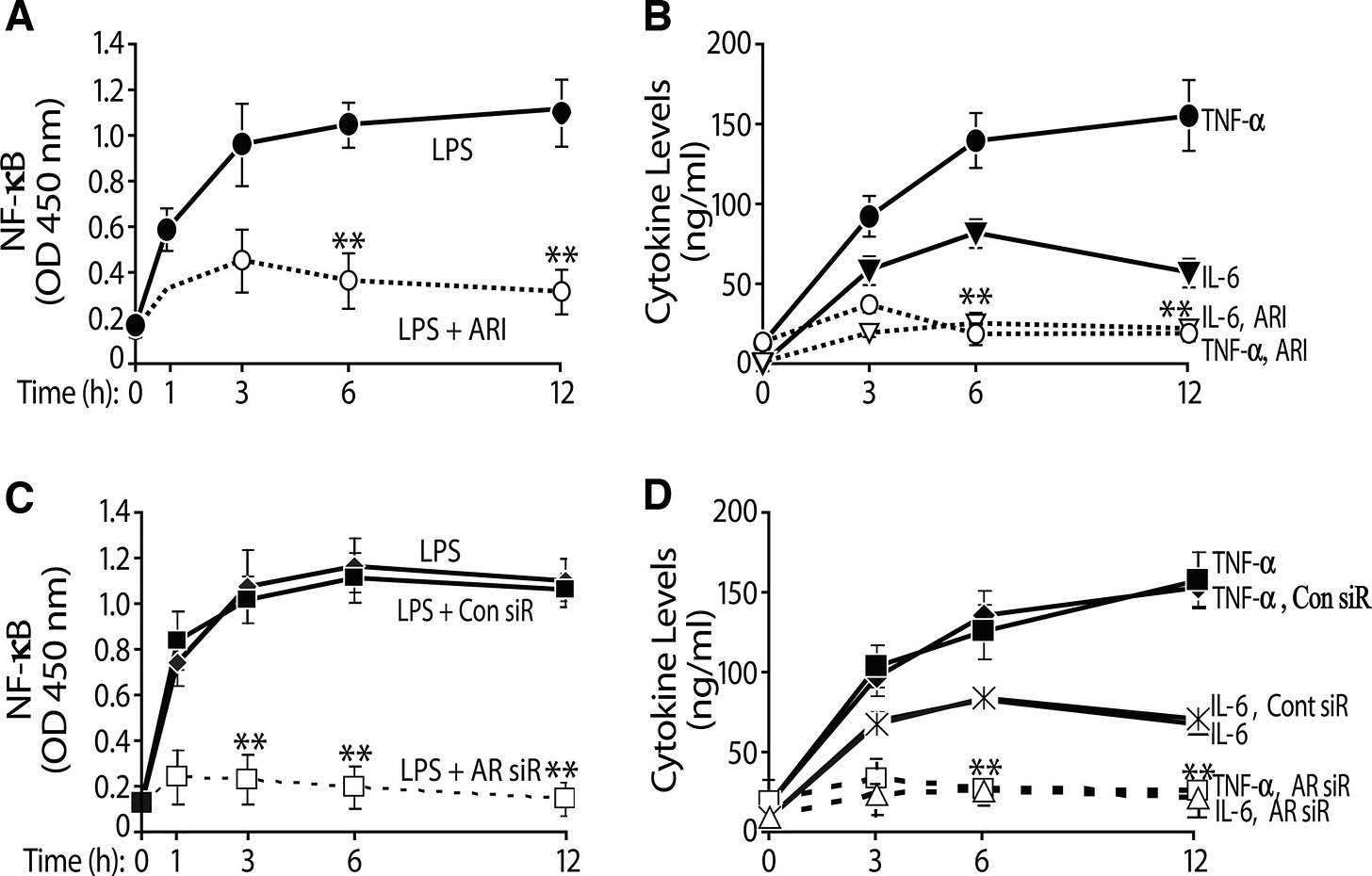
In 2006 it was shown that Cytokine Storm Heart Damage caused by Endotoxin proceeds via Aldose Reductase.34 Inhibiting this enzyme using the drug Sorbinil35 or by transfection with small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting Aldose Reductase reduced the inflammatory cascade.
Treatment of RAW264.7 macrophages with LPS (Endotoxin) led to a 6-fold increase in NF-κB activity within 6 hours of stimulation, and it remained elevated at this level for 12 hours. Treatment with the AR inhibitor Sorbinil suppressed the initial increase in NF-κB activity, and after 12 hours, the increase in NF-κB activity was not statistically different from the values obtained before LPS stimulation. Sorbinil treatment also blunted LPS-induced increases in TNF-α and IL-6
The authors emphasized the catalytic self-amplification of the damaging Cytokine release in Positive Feedback Loops leading to multiple organ failure.
March 2024 Update
Tracy Beth Høeg has written about the latest Pfizer Mandated Report on Myocarditis caused by their Jabs.36
August 2024 Update
Paywalled paper from Japan.37
Abstract
Background
The association between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) mRNA vaccines and myocarditis/pericarditis in the Japanese population has not been systematically investigated. This study was aimed at clarifying the association between SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines (BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273) and myocarditis/pericarditis as well as influencing factors by using the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database.
Methods
Reporting odds ratios (RORs) and 95 % confidence intervals (95 % CIs) for the association between the vaccines and myocarditis/pericarditis were calculated using data from the database (April 2004–December 2023). Age, sex, onset time, and outcomes in symptomatic patients were evaluated.
Results
The total number of reports was 880,999 (myocarditis: 1846; pericarditis: 761). The adverse events associated with the vaccines included myocarditis (919 cases) and pericarditis (321 cases), with the ROR [95 % CIs] being significant for both (myocarditis: 30.51 [27.82–33.45], pericarditis: 21.99 [19.03–25.40]). Furthermore, the ROR [95 % CIs] of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 were 15.64 [14.15–17.28] and 54.23 [48.13–61.10], respectively, for myocarditis, and 15.78 [13.52–18.42] and 27.03 [21.58–33.87], respectively, for pericarditis. Furthermore, most cases were ≤30 years or male. The period from vaccination to onset was ≤8 days, corresponding to early failure type based on analysis using the Weibull distribution. Outcomes were recovery or remission for most cases; however, they were severe or caused death in some cases.
Conclusion
In the Japanese population, SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination was significantly associated with the onset of myocarditis/pericarditis. The influencing factors included age of ≤30 years and male. Furthermore, although most adverse events occurred early after vaccination, overall outcomes were goo
The Future
Myocarditis has a very poor 5-year prognosis for survival. Pfizer is monitoring that.
Thanks to Hart group38 for bringing another Autopsy report39 from Japan to my attention.
It was conducted on a 40-year-old man who suddenly experienced Tachycardia and lost consciousness 2 days after his second Pfizer jab. His wife ordered the Autopsy which found Myocarditis with inflammatory infiltrates were predominantly composed of CD68-positive histiocytes mixed with a small number of CD8-positive T cells. There were relatively few CD4-positive T cells and CD20-positive B cells, and no CD138-positive plasma cells were observed.
January 2025 Update
Thanks to the Defender40 for alerting me to a “new” study41 of Jab induced Myocarditis in 206 people in the state of Victoria, published 13 January 2025 in the Medical Journal of Australia.
It appears publication of this study has been deliberately delayed.
Received 25 May 2023, accepted 8 April 2024.
Supplementary material is available from the Wiley publishers.42
The authors suggest
A threefold Troponin increase could be used as a threshold for risk stratification of people with COVID‐19 vaccine‐associated myocarditis, especially in hospitals with limited access to cMRI facilities.
This is a thoroughly disgusting recommendation that is all about economics!
June 2025 Update
Adding a paper published in August 2024 where CD3 and CD68 staining was used, the same as Nushida et al. in 2023.
Balbona et al. displays43 this table of the stains they used for the Autopsy of a previously healthy 34-year-old man, who suffered 16 days after his jab “acute inflammation, sudden Thoracic Aortic Dissection, and Pericardial Tamponade, rapidly leading to his death.”
See also my article on Aortic Dissection.44
European Medicines Agency Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee. Periodic Safety Update Report. Tozinamarem (Comirnaty) covering the period 19 December 2021 to 18 June 2022. Published January 2023.
Wong M-L, et al. 2003. Identification, characterization, and gene expression profiling of endotoxin-induced myocarditis. https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.2336220100
Shi H, et al. 2021. Inhibition of calpain reduces cell apoptosis by suppressing mitochondrial fission in acute viral myocarditis. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10565-021-09634-9
Wang R, et al. 2019. Leonurine alleviates LPS-induced myocarditis through suppressing the NF-кB signaling pathway. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0300483X18307066
Cheng Z, et al. 2014. Protective Role of the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway in a Mouse Model of Viral Myocarditis. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0112719
Ronaldson KJ et al, 2010. Diagnostic characteristics of clozapine-induced myocarditis identified by an analysis of 38 cases and 47 controls. https://www.psychiatrist.com/jcp/schizophrenia/psychotic-disorders/diagnostic-characteristics-clozapine-induced-myocarditis/
Seko Y, et al. 2002. Expression of tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily costimulatory molecules CD27L, CD30L, OX40L and 4-1BBL in the heart of patients with acute myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1054880702001011
Liu G, et al. Metformin attenuated endotoxin-induced acute myocarditis via activating AMPK. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1567576917301364
Patone M, et al. 2022. Risk of Myocarditis After Sequential Doses of COVID-19 Vaccine and SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Age and Sex. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.059970
Baumeier C, et al. 2022. Intramyocardial Inflammation after COVID-19 Vaccination: An Endomyocardial Biopsy-Proven Case Series. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/23/13/6940
Ehrlich P, et al. 2021. Biopsy-proven lymphocytic myocarditis following first mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in a 40-year-old male: case report. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8419377/
Schwab C, et al. 2022. Autopsy‑based histopathological characterization of myocarditis after anti‑SARS‑CoV‑2‑vaccination. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00392-022-02129-5
Kadwalwala M, et al. 2021. Multimodality imaging and histopathology in a young man presenting with fulminant lymphocytic myocarditis and cardiogenic shock after mRNA-1273 vaccination. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8634223/
Nagasaka T, et al. 2021. Acute myocarditis associated with COVID-19 vaccination: A case report. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8639400/
Onishi N, et al. Fulminant myocarditis with complete atrioventricular block after mRNA COVID-19 vaccination: A case report. https://www.journalofcardiologycases.com/article/S1878-5409(23)00005-1/fulltext
Buergin N, et al. 2023. Sex-specific differences in myocardial injury incidence after COVID-19 mRNA-1273 Booster Vaccination. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/ejhf.2978
Verma AK, Lavine KJ, Lin C-Y. 2021. Myocarditis after Covid-19 mRNA vaccination. https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMc2109975
Choi S et al. 2021. Myocarditis-induced Sudden Death after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Korea: Case Report Focusing on Histopathological Findings. https://jkms.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e286
Nushida H, et al. 2023. A case of fatal multi-organ inflammation following COVID-19 vaccination. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1344622323000548
Mörz M. 2022. A Case Report: MultifocalNecrotizing Encephalitis andMyocarditis after BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccination against COVID-19. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/10/10/1651
Beck A, et al. 2023. Emergence of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike protein at thevaccination site. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/iid3.827
Jiménez SA, et al. 2004. Dialysis-associated systemic fibrosis (nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy): Study of inflammatory cells and transforming growth factor β1 expression in affected skin. Arthritis and Rheumatism. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/art.20362
Di Gregorio GB, et al. 2005. Expression of CD68 and Macrophage Chemoattractant Protein-1 Genes in Human Adipose and Muscle Tissues: Association With Cytokine Expression, Insulin Resistance, and Reduction by Pioglitazone. https://diabetesjournals.org/diabetes/article/54/8/2305/13742/Expression-of-CD68-and-Macrophage-Chemoattractant
Zhang T, et al. 2012. Inhibition of Na/K-ATPase promotes myocardial tumor necrosis factor-alpha protein expression and cardiac dysfunction via calcium/mTOR signaling in endotoxemia. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00395-012-0254-8
Boyd JH, et al. 2008. S100A8 and S100A9 Mediate Endotoxin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Dysfunction via the Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/circresaha.107.167544
Srjevovic IM and Lukic ML. 2021. Galectin-3 in T cell-mediated immunopathology and autoimmunity. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S016524782100047X
Zhang W, et al. 2015. Necrotic Myocardial Cells Release Damage‐Associated Molecular Patterns That Provoke Fibroblast Activation In Vitro and Trigger Myocardial Inflammation and Fibrosis In Vivo. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/JAHA.115.001993
Lo T-Z, et al. 2021. Galectin-3 promotes noncanonical inflammasome activation through intracellular binding to lipopolysaccharide glycans. https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2026246118
Zheng X, et al. The Role and Mechanism of Pyroptosis and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Sepsis: A Review. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8293747/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/pyroptosis
Bouffette S, et al. 2023. Targeting galectin-3 in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases. https://www.cell.com/trends/pharmacological-sciences/fulltext/S0165-6147(23)00126-8
Xu H, et al. 2010. The Alarmin Cytokine, High Mobility Group Box 1, Is Produced by Viable Cardiomyocytes and Mediates the Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction via a TLR4/Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase γ Pathway. https://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/184/3/1492/82514/The-Alarmin-Cytokine-High-Mobility-Group-Box-1-Is
Barmada A, et al. 2023. Cytokinopathy with aberrant cytotoxic lymphocytes and profibrotic myeloid response in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine–associated myocarditis. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciimmunol.adh3455
Ramana KV, et al. 2006. Endotoxin-Induced Cardiomyopathy and Systemic Inflammation in Mice Is Prevented by Aldose Reductase Inhibition. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.630830
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sorbinil
Keisuke Takada , Kazuaki Taguchi , Masaru Samura , Yuki Igarashi, Yuko Okamoto, Yuki Enoki , Koji Tanikawa, Kazuaki Matsumoto. 2024. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine-related myocarditis and pericarditis: An analysis of the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database. https://www.jiac-j.com/article/S1341-321X(24)00209-5/abstract
Hiroshi Minato, Akane Yoshikawa, Sho Tsuyama, Kazuyoshi Katayanagi, Satoaki Hachiya, Keisuke Ohta and Yasuhiro Myojo. 2024. Fatal arrythmia in a young man after COVID-19 vaccination: An autopsy report. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10843519/
Julia Smith, Silja Schrader, Hannah Morgan, Priya Shenton, Annette Alafaci, Nicholas Cox, Andrew J Taylor, James Hare, Bryn Jones, Nigel W Crawford, Jim P Buttery, Hazel J Clothier and Daryl R Cheng. 13 January 2025. Clinical phenotype of COVID‐19 vaccine‐associated myocarditis in Victoria, 2021–22: a cross‐sectional study. https://www.mja.com.au/journal/2025/222/1/clinical-phenotype-covid-19-vaccine-associated-myocarditis-victoria-2021-22
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.5694/mja2.52557
E. J. Balbona, Heather Hudson, Michael Morz and Janci Lindsay. 2024. Case Report. Case of Myocarditis, Pericarditis, and Fatal Aortic Dissection Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination. Biomed Sci Clin Res, 3(3):1-8.