Kidney Deaths from Jabbing - Update
More on the Mechanisms of Sudden Onset Kidney harms, often Fatal after Jabs
As well as Endotoxin, Escherichia coli bacteria produce Shiga-Like Toxin that kills people by destroying their Kidneys. How much Shiga-Like Toxin is in Jab Vials?
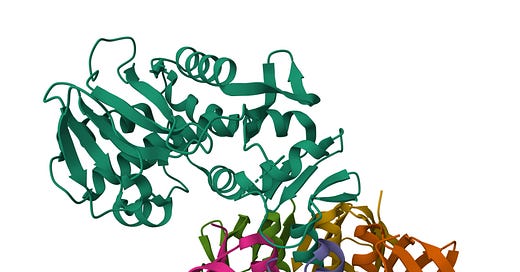
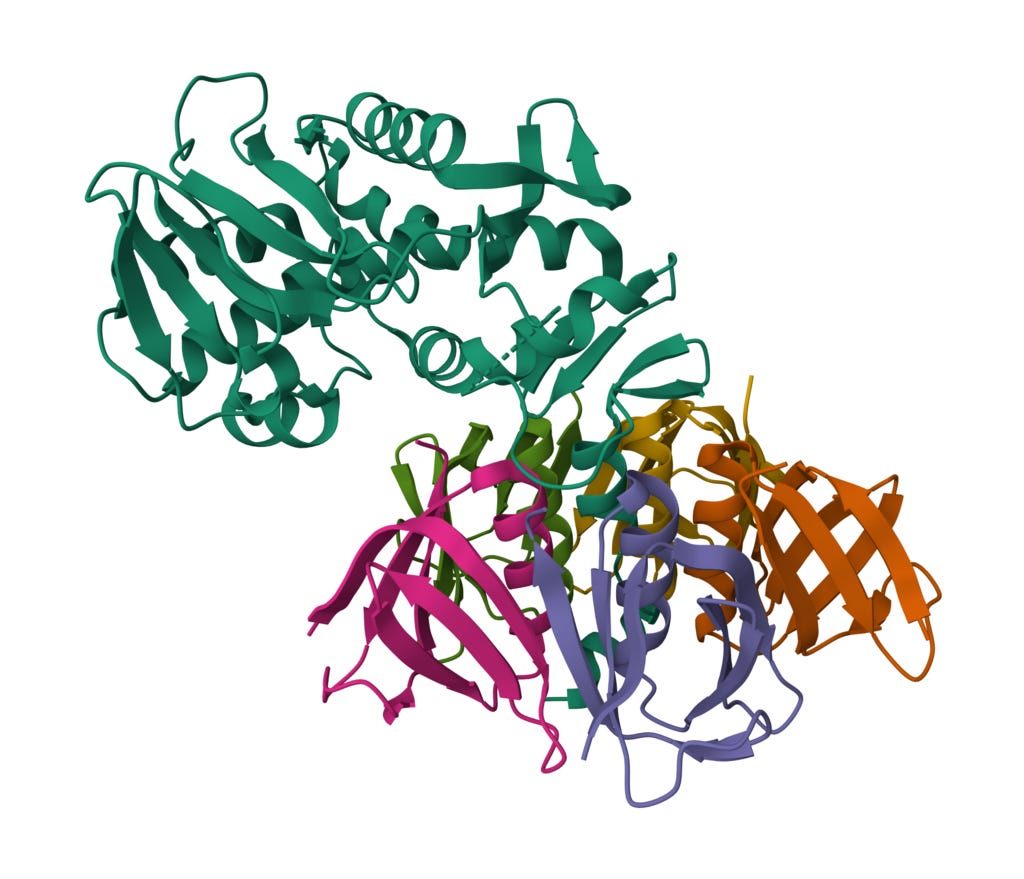
Here is a cartoon/ribbon representation of Shiga Toxin Type 2 (Stx2) from E. coli. A-subunit shown above (viridian), and B-pentamer subunits (multicolored) below.
Picture credit.1
Following my chosen focus, I checked the latest PubMed peer reviewed publications database. One has to tune searches after examining the collection, e.g. Sudden Kidney Injury is not as popular as Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). Acute Renal Failure (AFR) would also help with refining your search if you have time and iinclination.
Please see a couple of my earlier articles that have been updated.23
Starting with Kidney Endotoxin, I found 5,531 papers starting in 1927.
With Kidney Lipopolysaccharide, there are 5,661 papers from 1951
With Kidney LPS there are 4,745 papers starting in 1975
Euphemisms for Death
Reading about Sudden Kidney Failure one must remember that unless a Kidney Transplant could be arranged, most patients actually die.
John Beaudoin has gathered more data from Death certificates in Connecticut which shows a surge from 2020 to 2023 while Covid19 Deaths declined.
See more of John’s Research on Sudden Kidney Failure.45
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Those in the know understand at cellular level what Fatal Kidney Damage looks like and Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is one term used.
In 2006 Keepers and coworkers6 reported that Endotoxin and Shiga Toxin both destroy Kidneys and do it faster in Synergy.
Here we see their Figures 5 and 6 examining the effects on Mice Kidneys.
Note the Fibrin deposition7 and Red Blood Cell (RBC) congestion at low magnification.
Transmission Electron Microscopy in Figure 6 revealed endothelial cell damage and abnormal podocytes.
2019 paper on Feedback Loop Mechanism
One paper that caught my eye was a paper8 from Chinese researchers using Rats who concluded that:
Our results show for the first time that gut-derived Endotoxin, resulting from an increased intestinal permeability after severe renal IR (surgically induced Ischemia Reperfusion), subsequently amplifies intrarenal inflammatory response by activation renal TLR4 signaling.
Subscribers will recall that I have mentioned that a Jab in the Arm results in a Leaky Gut, which fits nicely with the impact on the Kidneys as just one of multiple organs damaged.9 IL1-β initiates the Positive Feedback Loop.10
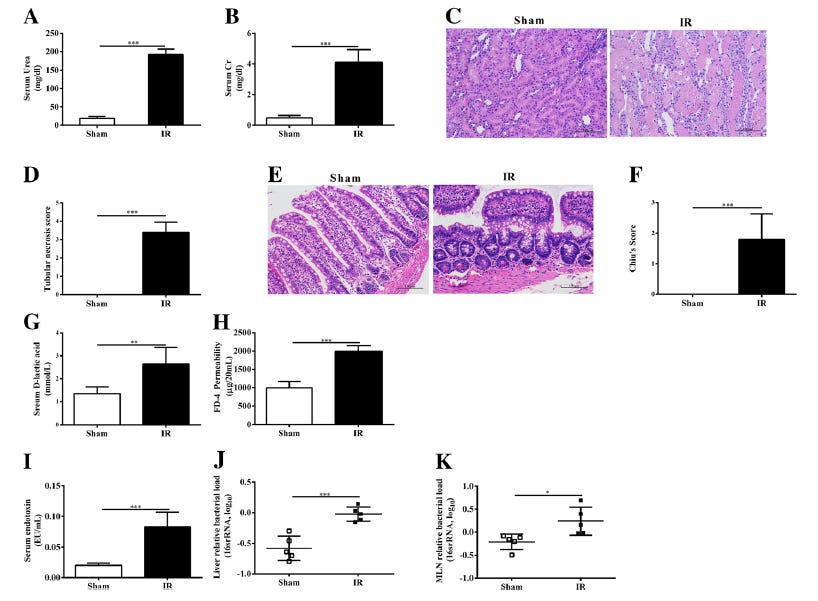
Here is their Figure 1.
Fig. 1
The intestinal consequences of renal IR induced AKI. Renal function was evaluated by serum urea (a) and creatinine (b) levels. Kidney and Ileum morphological alterations were evaluated by HE stained sections (original magnification× 200) and scored (c-f).
Intestinal permeability was evaluated by serum D-lactic (g) and an ex vivo isolated sac method (h).
The level of serum Endotoxin was measured using a Kinetic Turbidimetric LAL method (i).
Bacterial load was measured at Liver (j) and Mesenteric Lymph Nodes (k).
Bacterial load was represented by relative bacterial load in log as quantified by qPCR of 16S primer targets normalized to β-actin.
Higher values represent more bacteria. Data are expressed by mean ± SD.
The two-tailed unpaired t test was used (n = 5 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001
Note that this work showed that use of the Fluorinated aromatic antibiotic Norfloxacin11 did not help as hoped.
Cytokine Storm and Fatal Kidney Disease
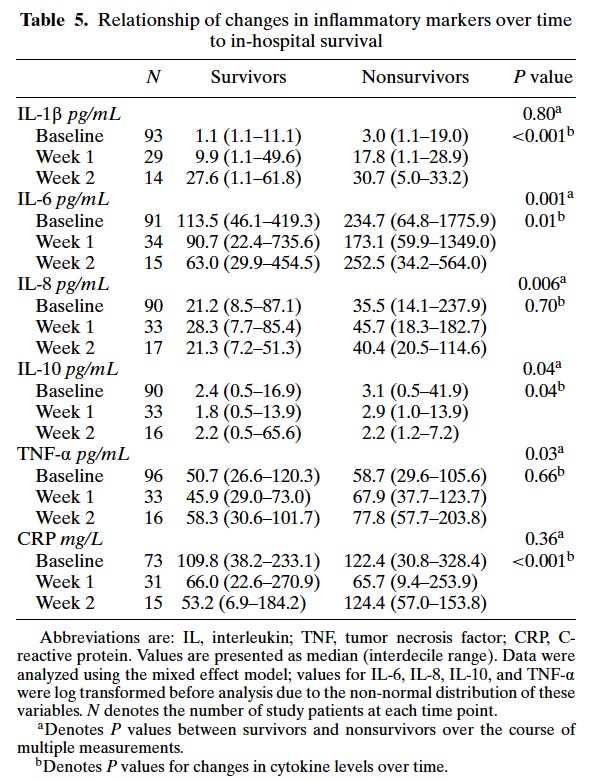
In 2004 Simmons and coworkers12 studied survivors versus non survivors and identified the key Cytokines.
Note IL-6 that I have discussed earlier13 and C Reactive Protein (CRP) and IL1-β are the most significant indicators.
Searching PubMed for “C Reactive Protein Endotoxin” finds 1,115 papers, “C Reactive Protein Lipopolysaccharide” 1,665 papers and “C Reactive Protein LPS” gives you 799 papers.
In 1990 new techniques were developed to follow Endotoxin and Sepsis Kidney damage by Suffredini and coworkers.14
Kidney Disase Classification Codes
Epidemiologists tend to get hung up on codes.
Here are some commonly used15 for Kidney Disease:
N00-N08 Glomerular diseases
N10-N16 Renal tubulo-interstitial diseases
N17-N19 Renal failure
N20-N23 Urolithiasis
N25-N29 Other disorders of kidney and ureter
N30-N39 Other diseases of urinary system
N99-N99 Other disorders of the genitourinary system
With more detail
Acute renal failure
Incl.:
acute renal impairment
N17.0 Acute renal failure with tubular necrosis
Tubular necrosis:
NOS
acute
renal
N17.1 Acute renal failure with acute cortical necrosis
Cortical necrosis:
NOS
acute
renal
N17.2 Acute renal failure with medullary necrosis
Medullary [papillary] necrosis:
NOS
acute
renal
N17.8 Other acute renal failure
N17.9 Acute renal failure, unspecified
N18 Chronic kidney disease
Incl.:
chronic renal failure
Use additional code, if desired, to identify underlying disease.
Use additional code, if desired, to identify presence of hypertension.
N18.1 Chronic kidney disease, stage 1
Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR (≥ 90 mL/min)
N18.2 Chronic kidney disease, stage 2
Kidney damage with mild decreased GFR (60-89 mL/min)
N18.3 Chronic kidney disease, stage 3
Kidney damage with moderately decreased GFR (30-59 mL/min)
N18.4 Chronic kidney disease, stage 4
Kidney damage with severely decreased GFR (15-29 mL/min)
N18.5 Chronic kidney disease, stage 5
End stage kidney disease:
in allograft failure
NOS
on dialysis
without dialysis or transplant
Renal retinitis (H32.8*)
Uraemic:
N18.9 Chronic kidney disease, unspecified
Chronic renal impairment
Chronic uraemia NOS
Diffuse sclerosing glomerulonephritis NOS
N19 Unspecified kidney failure
Incl.:
Renal insufficiency NOS
Uraemia NOS
Excl.:
kidney failure due to hypertension (I12.0)
uraemia of newborn (P96.0)
Reading the literature, Chronic Kidney Disease is a risk factor for Acute Kidney Injury and vice versa.
Hospital Acquired AKI is more common than previously thought.16
Mol* (D. Sehnal, S. Bittrich, M. Deshpande, R. Svobodová, K. Berka, V. Bazgier, S. Velankar, S.K. Burley, J. Koča, A.S. Rose (2021) Mol* Viewer: modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures (2021) Nucleic Acids Research 49:W431-W437 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab314) - PDB: 1R4P, Fraser, M.E., Fujinaga, M., Cherney, M.M., Melton-Celsa, A.R., Twiddy, E.M., O'Brien, A.D., James, M.N.G. Shiga Toxin Type 2 from Escherichia coli (2004) https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb1R4P/pdb Fraser, M.E., Fujinaga, M., Cherney, M.M., Melton-Celsa, A.R., Twiddy, E.M., O'Brien, A.D., James, M.N.G. Structure of Shiga Toxin Type 2 (Stx2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7. (2004) J Biol Chem 279: 27511-27517 https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M401939200 Visualization produced by Mol* as implemented on RCSB PDB. Mol* (D. Sehnal, S. Bittrich, M. Deshpande, R. Svobodová, K. Berka, V. Bazgier, S. Velankar, S.K. Burley, J. Koča, A.S. Rose (2021) Mol* Viewer: modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures (2021) Nucleic Acids Research 49:W431-W437 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab314) H.M. Berman, J. Westbrook, Z. Feng, G. Gilliland, T.N. Bhat, H. Weissig, I.N. Shindyalov, P.E. Bourne, The Protein Data Bank (2000) Nucleic Acids Research 28: 235-242 https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.235.
SV40 immortalized Kidney Cells damaged by Endotoxin as found in every Pfizer Jab
As a member of the DailyClout team, I took a keen interest in the court ordered release of Pfizer trial data as it was posted and discussed in our weekly teleconferences.
https://x.com/JohnBeaudoinSr
Tiffany R. Keepers, Mitchell A. Psotka, Lisa K. Gross, and Tom G. Obrig. 2006. A Murine Model of HUS: Shiga Toxin with Lipopolysaccharide Mimics the Renal Damage and Physiologic Response of Human Disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 3404-3414.
Conformal White Fibrin "Clots" are caused by Endotoxin in Jabs
I have previously pointed to Endotoxin induced Fibrosis, i.e. deposition of Fibrin in the Heart and Pericarditis that results in insoluble White Fibrin on the surface of the Heart.
Jiangtao Li, Krishna Rekha Moturi, Lirui Wang, Kun Zhang and Chen Yu. 2019. Gut derived-endotoxin contributes to inflammation in severe ischemic acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrology 20:16
Leaky Gut caused by Endotoxin in Jabs
Jab in the Arm, opens your Gut and lets Toxins invade your system.
Autoimmune Diseases caused by Endotoxin in mRNA Jabs include Myocarditis, Pericarditis Lupus
Recently I briefly mentioned that Endotoxin, as found in every vial of Moderna and Pfizer jab, causes Autoimmune Diseases.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Norfloxacin
EDITH M. SIMMONS, JONATHAN HIMMELFARB, M. TUGRUL SEZER, GLENN M. CHERTOW, RAVINDRA L. MEHTA, EMIL P. PAGANINI, SHARON SOROKO, STEPHANIE FREEDMAN, KAREN BECKER, DANIEL SPRATT, YU SHYR, and T. ALP IKIZLER, FOR THE PICARD STUDY GROUP. 2004. Plasma cytokine levels predict mortality in patients with acute renal failure. Kidney International, 65:1357-1365.
Drew Weissman Endotoxin induced Interleukin-6 Legacy
In my recent article I pointed to a new patent application by Drew Weissman and colleagues in which it was revealed that mRNA LNP jabs massively increased Endotoxin Interleukin-6 damage and death.
Endotoxin Supplier to the World for Human Jabbing Experiments
Meet the man in charge, Dr Anthony F. Suffredini.
https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en#/N30-N39
Anna C. Bendall, Emily J. See, Nigel D. Toussaint, Timothy Fazio, Sven-Jean Tan. 2022. Community-acquired versus hospital-acquired acute kidney injury at a large Australian metropolitan quaternary referral centre: incidence, associations and outcomes. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/imj.15787