Postmenopausal Haemorrhage after mRNA jabs most likely caused by Endotoxin
VAERS and other databases are likely showing only a fraction of Women who have suffered this medical emergency caused by mass jabbing. Progesterone is the key.
Postmenopausal haemorrhage is something just less than half of Humanity will never suffer, so what can a man say about it?
Pfizer reports Thousands of cases
We know Women are more severely impacted by the mRNA jabs than men and this relates directly to the Endotoxin in each vial.1
To April 2022, Pfizer reported 338 different “Reproductive system and breast disorders” the following case numbers that show Women have suffered terrible disruption of their reproductive organs, especially their Uterus:
Postmenopausal haemorrhage 2,456
Uterine haemorrhage 231
Abnormal uterine bleeding 100
Cervix haemorrhage uterine 12
Uterine haematoma 7
Uterine spasm 204
Uterine leiomyoma 91, Uterine polyp 37, Uterine cyst 12
Uterine inflammation 36
Uterine hypertonus 29
Uterine disorder 26
Uterine enlargement 13
Uterine infection 8
Menopausal symptoms 238
Menopause 141
Premature menopause 58
Postmenopause 8
Menopausal disorder 7
Menopause delayed 6 - would someone explain that to us?
Heavy menstrual bleeding 27,685
Menstrual disorder 22,145
Menstruation irregular 15,083
Menstruation delayed 13,989
Dysmenorrhoea 13,904
Intermenstrual bleeding 12,424
Amenorrhoea 11,363
Polymenorrhoea 9,546
Oligomenorrhoea 3,437
Hypomenorrhoea 2,643
Menometrorrhagia 632
Endometriosis 337
Uterine pain 270
Ovulation disorder 96
Vaginal haemorrhage 4,699
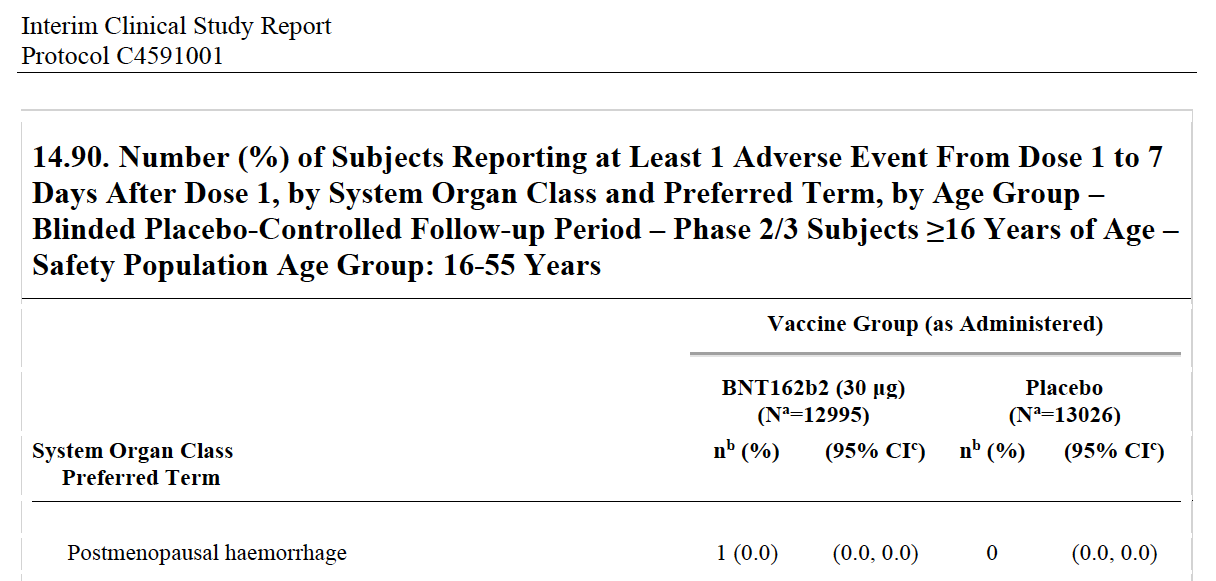
Pfizer Reported Postmenopausal Haemorrhage in its Trial
It will come as no surprise to many that Pfizer reported Postmenopausal Haemorrhage within 7 days of its jab during the clinical trial. Thanks to the judge who ordered release of the Trial Data 75 years ahead of the plan!
Comparison with other Covid19 jabs
Menstrual disorders have been caused by numerous Covid19 jabs including a study in 2022 from Iran comparing Sinopharm, AstraZeneca, Sputnik V, and Covaxin.2
Another study from Iran3 appeared in 2023 based on a very small sample of women.
A study4 of young women tried to suggest the observed menstrual irregularities were “psychological”.
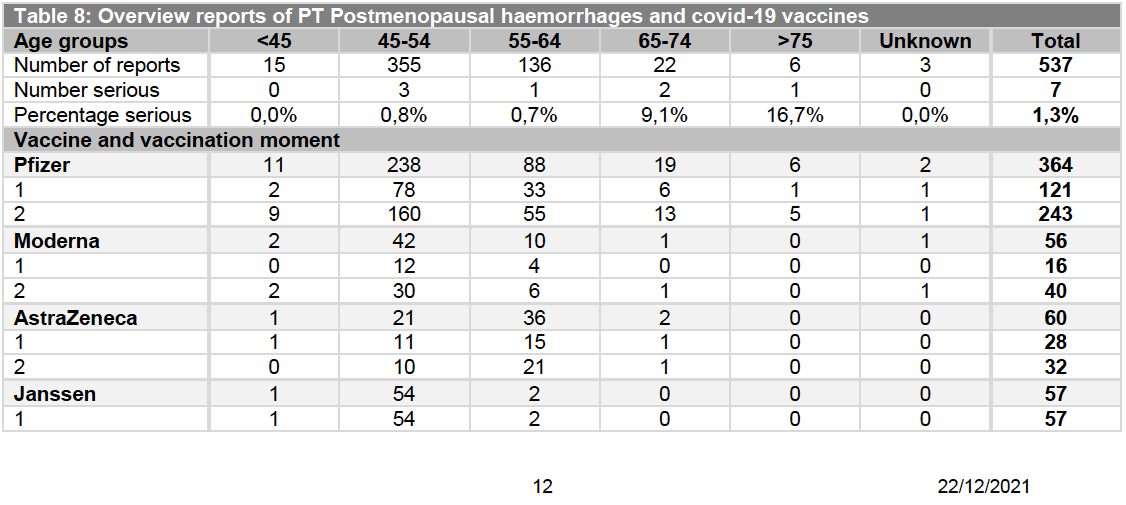
Official data5 was available by 1 December 2021, from authorities in The Netherlands, showing a very clear warning signal, reported the following mRNA jab cases of Postmenopausal Haemorrhage:
Pfizer 364, including 6 ladies aged over 75
Moderna 56
Both brands showed higher case numbers after the 2nd jab.
Note that cases do not correlate with amount of mRNA in the different brands.
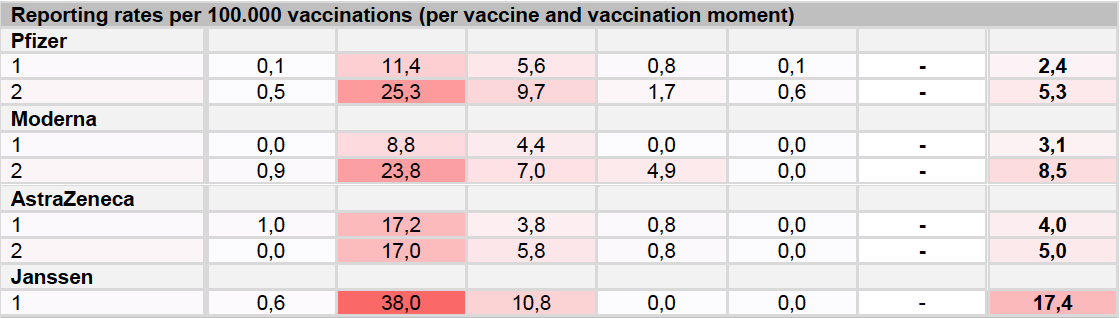
Reporting rates per 100,000 jabs for the various brands are shown.
Selected Publications on Postmenopausal Bleeding related to Endotoxin
Because the subject is complicated, here is a quick survey of papers on Covid19 jab induced postmenopausal disruption of the Uterus, looking for proposed mechanisms.
Endotoxin is routinely used to induce preterm birth and a very useful review across many species reports on the hormone disruption, including Progesterone.6
Merchant wrote about it in 2021 but offered little with regard to mechanisms.7
Lee and coworkers pointed to the need to further investigate the large number of Postmenopausal Haemorrhage victims of Covid19 jabs.8
A large recent survey in Sweden measured the incidence of Menstrual Disorders in Sweden.9
Estrogen decline with Age makes Women more vulnerable to Inflammation
I previously briefly mentioned10 the possibility that Endotoxin is the cause of Postmenopausal Haemorrhage and have not so far heard of a more convincing explanation.
Postmenopausal women have an increased Sepsis Endotoxin mortality rate compared to pre-menopausal women.1112
A very useful review by Vázquez-Martínez and coworkers13 covers a number of crucial hormones, including Estrogen and Progesterone and states:
Postmenopausal women and women with induced menopause due to surgical elimination of the ovaries have reduced levels of B cells and anti-inflammatory cytokines, IL-4, and interferon γ (IFNγ), while NK cell activity and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL2, and IL-6 are increased.
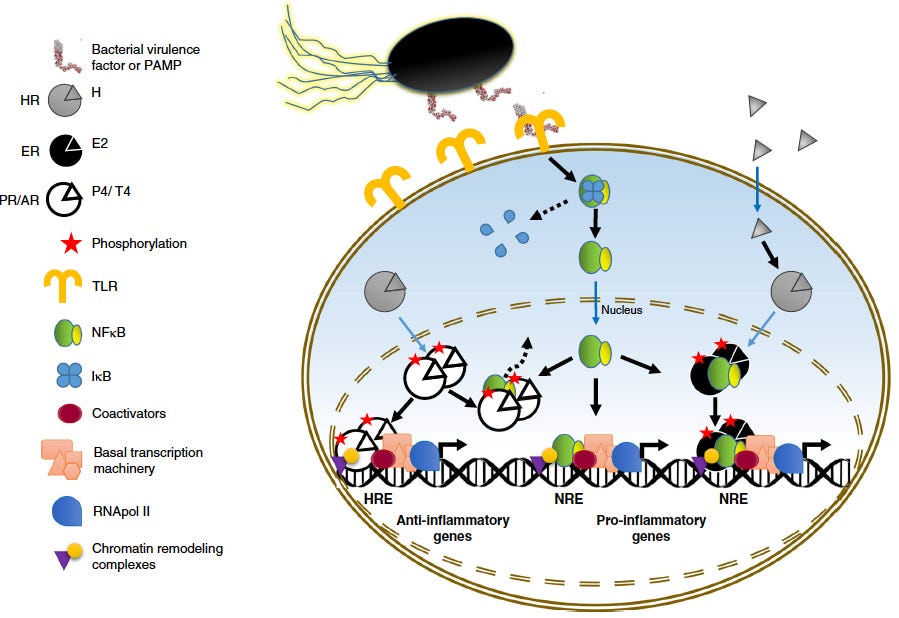
Their scheme shows how Gram negative bacteria, or as found in every vial of mRNA jab, the Endotoxin on the cell walls, initiates disaster through the Toll-Like Receptors.
In their scheme
HR = HR steroid hormone Receptor
ER = Estrogen Receptor
PR/AR = Progesterone Receptor / Androgen Receptor
TLP = Toll-Like Receptor
NFϰB = Nuclear factor kappa B
IϰB = Inhibitor of Nuclear factor kappa B
NRE = Nuclear Response Elements
RNApol II = RNA polymerase II
Progesterone impacted by Endotoxin
Shedding of the Uterus lining during Menstruation is primed by reduction in Progesterone expression.14
The RelA(p65) subunit of NF-κB and the Progesterone Receptor interact with each other, exhibiting mutual repression.15 Activation of NF-κB by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α also results in repression of the Progesterone Receptor (PR), while PR is able to repress Tumor Necrosis F actor-α-induced NF-κB activity.
As pointed out by James Thorp16 and his team, Decidual Casts “may occur when the cessation of Progesterone levels results in loss of support for the decidualized endometrial lining [3]”.
Clearly the Endotoxin from jabs disturbs this balance.
Activation of Estrogen receptor α by Hormone Replacement Therapy in postmenopausal women inhibits NF-κB mediated inflammation response and cytokine production.17
A useful review of the critical role of Progesterone in Menstruation gives many references.18
The definitive proof that Endotoxin reduces Progesterone was performed by measuring the association between systemic levels of Lipopolysaccharide-Binding Protein (LBP), a marker of endotoxin exposure, and levels of inflammation in the ovary (follicular fluid IL-6), plus steroid hormone production in 45 women undergoing IVF treatment.19 The authors proposed that:
disturbance in gut wall integrity (“leaky gut”) seen in these conditions may result in the passage of bacterial endotoxin (LPS) from the colonic lumen into the circulation that may initiate inflammation in the ovary and subsequently impair hormone production.
Endotoxin related to other Uterine disorders
Estradiol attenuates Endotoxin poisoning in Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes20 and Macrophages.21
Direct effects of Endotoxin on the Uterus have been studied.22
Contrary to the previous discussion of a protective role of Estrogen, hitting Uterine macrophages with bacterial Endotoxin induces production of biologically active proinflammatory IL-1β. High doses of Estradiol enhance Endotoxin-induced IL-1β expression in an estrogen receptor-dependent manner.
Endotoxin has been related to female infertility.23
Khan and coworkers studied Endotoxin levels in menstrual blood in TLR4-mediated growth of Endometriosis.24
Further work measured pro-inflammatory markers in endometriosis.25
Update September 2023
Researchers in Norway have published on jab induced vaginal bleeding following the jabs.26 The authors appear to be unaware of the likely mechanism I have discussed.
Abdollahi A, et al. 2022. Comparison of side effects of COVID-19 vaccines: Sinopharm, AstraZeneca, Sputnik V, and Covaxin in women in terms of menstruation disturbances, hirsutism, and metrorrhagia: a descriptive-analytical cross-sectional study. https://www.ijfs.ir/article_252289.html
Rastegar T, et al. 2023. COVID-19 vaccine side effects on menstrual disturbances among Iranian women. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10085868/
Kareem R, et al. 2022. The effect of COVID-19 vaccination on the menstrual pattern and mental health of the medical students: A mixed-methods study from a low and middle-income country. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0277288
Netherlands Pharmacovigilance Centre Lareb. 1 December 2021. Menstrual disorders and postmenopausal bleeding after administration of COVID-19 vaccines. https://www.lareb.nl/media/uoneih5z/signals_2021_menstrual_disorders-and-postmenopausal_bleeding-and-covid-19-vaccines.pdf
Bidne KL, et al. 2018. Disruption of female reproductive function by endotoxins. https://rep.bioscientifica.com/view/journals/rep/155/4/REP-17-0406.xml?body=pdf-54019
Merchant H. CoViD-19 post-vaccine menorrhagia, metrorrhagia or postmenopausal bleeding and potential risk of vaccine-induced thrombocytopenia in women. https://www.bmj.com/content/373/bmj.n958/rr-2
Lee KMN, et al. 2022. Investigating trends in those who experience menstrual bleeding changes after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abm7201
Ljung R, et al. 2023. Association between SARS-CoV-2 vaccination and healthcare contacts for menstrual disturbance and bleeding in women before and after menopause: nationwide, register based cohort study. https://www.bmj.com/content/381/bmj-2023-074778
Bouman A, et al. 2005. Sex hormones and the immune response in humans. https://academic.oup.com/humupd/article/11/4/411/874969
Angele MK, et al. 2006. Gender and sex hormones influence the response to trauma and sepsis: potential therapeutic approaches.
Vázquez-Martínez ER, et al. 2018. Sexual dimorphism in bacterial infections. https://bsd.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13293-018-0187-5
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/24562-progesterone
Kalkhoven E, et al. Negative Interaction between the RelA(p65) Subunit of NF-κB and the Progesterone Receptor. https://www.jbc.org/article/S0021-9258(17)45524-4/fulltext
Tiffany Parotto, James A. Thorp, Brian Hooker, Paul J. Mills, Jill Newman, Leonard Murphy, Warren Geick, Dan McDyer, Raphael B. Stricker, Sue Peters, Maureen McDonnell, Heather Ray, Christiane Northrup. 2022. COVID-19 and the Surge in Decidual Cast Shedding. G Med Sci. 3(1):107-117
Al-Lami RA, et al. 2020. Sex hormones and novel corona virus infectious disease (COVID-19). https://www.mayoclinicproceedings.org/article/S0025-6196(20)30518-8/fulltext
Critchley HOD, et al. 2006. Regulation of human endometrial function: mechanisms relevant to uterine bleeding. https://rbej.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7827-4-S1-S5
Tremellen K, et al. 2014. Metabolic endotoxaemia – a potential novel link between ovarian inflammation and impaired progesterone production. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.3109/09513590.2014.994602
Pioli PA, et al. 2007. Estradiol Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced CXC Chemokine Ligand 8 Production by Human Peripheral Blood Monocytes. https://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/179/9/6284/38167
Murphy AJ, et al. 2009. Estradiol Regulates Expression of Estrogen Receptor ERα46 in Human Macrophages. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2678254/
Pioli PA, et al. 2006. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced IL-1β Production by Human Uterine Macrophages Up-Regulates Uterine Epithelial Cell Expression of Human β-Defensin 2. https://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/176/11/6647/37358/Lipopolysaccharide-Induced-IL-1-Production-by
Deb, et al. 2004. Gram-Negative Bacterial Endotoxin- Induced Infertility: A Birds Eye View. https://karger.com/goi/article-abstract/57/4/224/151858/Gram-Negative-Bacterial-Endotoxin-Induced
Khan KN, et al. 2010. Escherichia coli contamination of menstrual blood and effect of bacterial endotoxin on endometriosis. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0015028210006916
Tortorella C, et al. 2014. Interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, and tumor necrosis factor α in menstrual effluents as biomarkers of chronic endometritis. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0015028213031154
Blix K, et al. Unexpected vaginal bleeding and COVID-19 vaccination in nonmenstruating women. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adg1391




According to my safety signals, it is much more common after Pfizer shots than after Moderna after age adjustment.
https://www.pervaers.com/?v=PFI&q=*menstr
https://www.pervaers.com/?v=MOD&q=*menstr
But surprisingly I am also seeing higher proportions among Johnson reports than among Moderna reports:
https://www.pervaers.com/?v=JAN&q=*menstr
I have now made this contribution free for all subscribers to read.
I am now convinced there is firm Evidence that jab disruption to Progesterone is a key driver of adverse effects in Women.
Thanks to all who have sent me comments and links to relevant data.
I deleted one comment because it contained incorrect content that could be misleading.