Frame-shifting Warning in 2014 from Nobel Prizer winner Katalin Karikó
She told us that Endotoxin would be in the all the Pfizer BioNTech jabs and warned about Frame Shifting creating "Potent cryptic T cell epitopes" caused by Ribosomal Frame-shifting
No surprises anymore in the greatest disaster deliberately injected into the arms of Billions. The paper by Mulroney and coworkers is unusual because its publication was obviously delayed (Received 25 January 2023, Accepted 31 October 2023, Published 06 December 2023).1 Quick, let’s look back to what Katalin Karikó said in 2014.2
Potent cryptic T cell epitopes may be generated when the IVT mRNA is translated in different frames owing to ribosomal frame-shifting or when translation is initiated either internally or from a CUG start codon [56–58].
Note Karikó stated optimistically that “Codon optimization should eliminate these important sources of antigenic peptides”. She was wrong!
Let us look at her references 56-58.
In 1999 Malarkannan and coworkers reported3 “out-of-frame” non-AUG translation initiation codons at the level of translational rather than DNA replication or transcription mechanisms. “This translation mechanism decoded the CUG initiation codon not as the canonical methionine but as the leucine residue, and its activity was independent of upstream translation initiation events.”
In 2002 Saulquin and coworkers4 investigated the Frame-shifting production of dangerous “Cryptic Epitopes” due to misreading of instructions during expression of proteins under mRNA instructions.
In 2003 Schwab and coworkers5 continued the investigation of this error extending into the so-called “non-coding” region of genomic code and its implications in Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) class I.
Frame-shifting causes Great Suffering
Severe Bleeding results from Frame-shifting as revealed by Human genome studies.6
Jabs have been developed exploiting Frame-shifting and “immunogenic frameshift peptide (FSP) neoantigens” have been used in clinical trials to see what happens.7
Furin Cleavage Site and Cancer Frame-shift
An exceptionally interesting link between the Bioweaponization tool known as the Furin Cleavage Site8 and Frame-shifting mutations is revealed in a review by Kazuhisa Nakayama.9 It is worth quoting a section:
this problem was overcome by the use of cell lines that are unable to produce functional furin ; namely, LoVo, a human colon carcinoma cell line, and RPE.40, a mutant cell line derived from Chinese-hamster ovary (CHO) cells. LoVo cells were shown to produce precursor forms of the insulin receptor and hepatocyte-growth-factor receptor [99], both of which have a consensus furin cleavage site (see Table 2). My colleagues and I have since shown that furin transfection of LoVo cells restores normal processing of these pro-receptors [100]. Cloning of furin cDNAs has revealed that LoVo cells have two mutant alleles of the fur gene; one is a frameshift mutation in the Homo B domain, and the other is a point mutation of a conserved Trp residue at position 547 of the Homo B domain to Arg [40,41]. Further, Moehring and co-workers [101-103] isolated RPE.40 as one of mutant strains of CHO cells that exhibits resistance to Pseudomonas exotoxin. This group showed that it was also resistant to diphtheria toxin and some enveloped viruses. Since the bacterial toxins and envelope glycoproteins of the viruses have a consensus furin cleavage site (see Table 2), they transfected a furin expression vector into RPE.40 cells and showed that the transfected cells became as sensitive to the toxins as wild-type CHO cells and were capable of cleaving viral glycoprotein precursors [104]. Cloning of furin cDNAs and sequence analysis of the fur gene in RPE.40 cells has revealed that one allele has a Cys-to-Tyr mutation at position 303 (position 196 in mature furin) near the oxyanion hole Asn residue and the other has a point mutation in an intron sequence that causes a splicing defect [105]. In these furin-deficient cell lines, all but one of the exogenously expressed precursor proteins, which had been previously shown to be cleaved by furin in cellular co-expression and}or in itro studies, failed to undergo cleavage. Taken together with the fact that furin mRNA is detected in all tissues and cell lines examined so far, the data using the furin-deficient cell lines demonstrates that furin is involved in the proteolytic processing of most precursor proteins with the consensus furin cleavage sequence. The only exception is the envelope glycoprotein precursor (gp160) of HIV-1.
Frame-shifting and Crohn’s Disease
Ogura and coworkers10 have shown that Frame-shifting is associated with Crohn’s Disease. Once again we find a link to Endotoxin.
Wild-type NOD2 activates nuclear factor NF-kB, making it responsive to bacterial lipopolysaccharides; however, this induction was deficient in mutant NOD2. These results implicate NOD2 in susceptibility to Crohn's disease, and suggest a link between an innate immune response to bacterial components and development of disease.
Frame-shifting and Granulomatous Histiocytosis
Granulomatous Histiocytosis prominent in the nasal area, mimicking Rhinoscleroma and Rosai-Dorfman syndrome.11
Breast Cancer Risk increased by Frame-shifting
3300 del A-1061 Ter BRCA1 mutation at exon 11 caused oxidative stress through superoxide dismutase activity inhibition (P < 0.05) and calcium propionate effected on superoxide dismutase activity in breast cancer cells and may lead to breast carcinogenesis.12
Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha-nduced Protein 3 (TNFAIP3, A20) frameshift mutation has been linked to an Autoimmune Disease–causing mechanism in both Peripheral Tissues and the Central Nervous System in a man suffering Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.13
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Frameshift insertion mutation of the gene for Copper-Zinc Superoxide Dismutase in UK families with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.14
Autosomal dominant Spinocerebellar Ataxia
Autosomal dominant Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 48 found to be inherited due to Frame-shift mutation.15
Craniofacial Dysmorphism, Skeletal Anomalies and Mental Retardation
Inherited Frame-shift mutation in Amish Community causes Craniofacial Dysmorphism, Skeletal Anomalies, and Mental Retardation.16
Rhabdomyolysis
Rhabdomyolysis linked to Frame-shift.17
Atopic Dermatitis and Eczema-associated asthma
Increased Allergy.18
International response has been swift
The demonstration that the mRNA jabs create a toxic soup of antigenic proteins has been swift.19
I will add more references as we delve further.
Going back to August 2022, Kevin McKernan was fully on top of the problem of translation errors from the GMO mRNA.20 He just published an update.21
Here is nice a thread by Mathew Aldred.22
Mathew led me to Igor Chudov explaining more about the Frame-shifting.23
Jessica Rose has produced a very nice review of the technical details of Frame-shift mechanisms and consequences.24
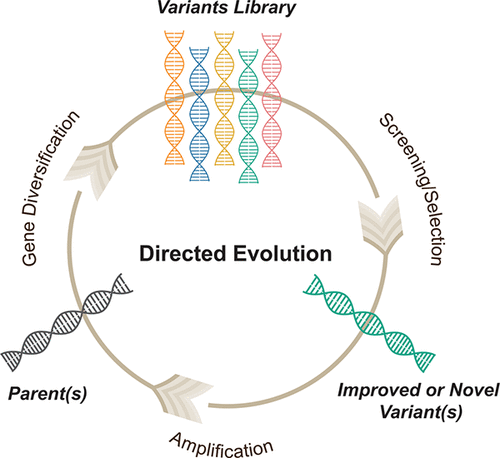
We need to stop this technology and all “Gain of Function” now called “Directed Evolution” madness25 now!
Thomas E. Mulroney, Tuija Pöyry, Juan Carlos Yam-Puc, Maria Rust, Robert F. Harvey, Lajos Kalmar, Emily Horner, Lucy Booth, Alexander P. Ferreira, Mark Stoneley, Ritwick Sawarkar, Alexander J. Mentzer, Kathryn S. Lilley, C. Mark Smales, Tobias von der Haar, Lance Turtle, Susanna Dunachie, Paul Klenerman, James E. D. Thaventhiran and Anne E. Willis. 2023. N1-methylpseudouridylation of mRNA causes +1 ribosomal frameshifting. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06800-3
Ugur Sahin, Katalin Karikó and Özlem Türeci. mRNA-based therapeutics - developing a new class of drugs. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrd4278
Malarkannan, S. et al. 1999. Presentation of out-of-frame peptide/MHC class I complexes by a novel translation initiation mechanism. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1074761300800679
Xavier Saulquin, Emmanuel Scotet, Lydie Trautmann, Marie-Alix Peyrat, Franck Halary, Marc Bonneville, Elisabeth Houssaint. 2002. Brief Definitive Report. +1 Frameshifting as a Novel Mechanism to Generate a Cryptic Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitope Derived from Human Interleukin 10. https://rupress.org/jem/article/195/3/353/8312/1-Frameshifting-as-a-Novel-Mechanism-to-Generate-a
Schwab, S. R. et al. 2003. Constitutive display of cryptic translation products by MHC class I molecules. https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.1085650
Dugarte MEC, Dørum E, Skarpen E, Koehler C, Thiede B, Morth JP, Myklebust CF, Pinotti M, Bernardi F, Sandset PM and Skretting G. 2015. FVII deficiency: unveiling the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying three model alterations (missense, deletion, extension) of the FVII catalytic domain. International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis 13 (Suppl. 2) (2015) 1–997.
Kloor M, Reuschenbach M, Pauligk C, Julia Karbach; Mohammad-Reza Rafiyan; Salah-Eddin Al-Batran; Mirjam Tariverdian; Elke Jäger; Magnus von Knebel Doeberitz. 2020. A Frameshift Peptide Neoantigen-Based Vaccine for Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancers: A Phase I/IIa Clinical Trial. https://aacrjournals.org/clincancerres/article/26/17/4503/82705/A-Frameshift-Peptide-Neoantigen-Based-Vaccine-for
Pfizer used Synthetic Life derived from US Bioweapons research for its mRNA trials
If you want to turn Coronavirus into a more lethal weapon, you need to make sure its entry into Human cells is enhanced. The Covid19 virus Spike protein comes as a trimer of intertwined proteins that lock onto membrane bound ACE2 enzyme that is expressed in many cell types throughout the body.
Kasuhiza Nakayama. 1997. Furin : a mammalian subtilisin/Kex2p-like endoprotease involved in processing of a wide variety of precursor proteins. Biochem. J. (1997) 327, 625-635
Yasunori Ogura, Denise K. Bonen, Naohiro Inohara, Dan L. Nicolae, Felicia F. Chen, Richard Ramos, Heidi Britton, Thomas Moran, Reda Karaliuskas, Richard H. Duerrk, Jean-Paul Achkar, Steven R. Brant, Theodore M. Bayless, Barbara S. Kirschner, Stephen B. Hanauer, Gabriel Nunez and Judy H. Cho. 2001. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. https://www.nature.com/articles/35079114
Alexandre Bolze , Avinash Abhyankar, Audrey V. Grant, Bhavi Patel, Ruchi Yadav, Minji Byun, Daniel Caillez, Jean-Francois Emile, Marçal Pastor-Anglada, Laurent Abel, Anne Puel, Rajgopal Govindarajan, Loic de Pontual, Jean-Laurent Casanova. 2012. A Mild Form of SLC29A3 Disorder: A Frameshift Deletion Leads to the Paradoxical Translation of an Otherwise Noncoding mRNA Splice Variant. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0029708
Pongsavee M. 2019. Effects of 3300 del A-1061 Ter BRCA1 frameshift mutation and calcium propionate on oxidative stress and breast carcinogenesis. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6627784/
Ruonan Duan, Qi Liu, Jiangxia Li, Xianli Bian, Qianqian Yuan, Yan Li, Feng Long, Shang Gao, Shijun Wei, Pengyu Li, Fei Gao, Wenjie Sun, Xi Li and Qiji Liu. 2019. A De Novo Frameshift Mutation in TNFAIP3 Impairs A20 Deubiquitination Function to Cause Neuropsychiatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10875-019-00695-4
R W Orrell, J J Habgood, I Gardiner, A W King, F A Bowe, R A Hallewell, S L Marklund, J Greenwood, R J Lane and J deBelleroche. 1997. Clinical and functional investigation of 10 missense mutations and a novel frameshift insertion mutation of the gene for copper-zinc superoxide dismutase in UK families with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9065559/
Chen, HY., Hsu, CL., Lin, HY. et al. Clinical and functional characterization of a novel STUB1 frameshift mutation in autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxia type 48 (SCA48). https://jbiomedsci.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12929-021-00763-1
Baozhong Xin, Erik G. Puffenberger, Susan Turben, Haiyan Tan, Aimin Zhou, and Heng Wang. 2009. Homozygous frameshift mutation in TMCO1 causes a syndrome with craniofacial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, and mental retardation. https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.0908457107
Chikako Ishikawa, Hiroshi Ozaki, Toshiaki Nakajima, Toshihiro Ishii, Saburo Kanai, Saeko Anjo, Kohji Shirai and Ituro Inoue. 2004. A frameshift variant of CYP2C8 was identified in a patient who suffered from rhabdomyolysis after administration of cerivastatin. https://www.nature.com/articles/jhg200492
Padraic G Fallon, Takashi Sasaki, Aileen Sandilands, Linda E Campbell, Sean P Saunders, Niamh E Mangan, John J Callanan, Hiroshi Kawasaki, Aiko Shiohama, Akiharu Kubo, John P Sundberg, Richard B Presland, Philip Fleckman, Nobuyoshi Shimizu, Jun Kudoh, Alan D Irvine, Masayuki Amagai and W H Irwin McLean. 2009. A homozygous frameshift mutation in the mouse Flg gene facilitates enhanced percutaneous allergen priming. https://www.nature.com/articles/ng.358
David Wiseman, L. Maria Gutschi, David J. Speicher, Jessica Rose, Kevin McKernan. 2023. Ribosomal frameshifting and misreading of mRNA in COVID-19 vaccines produces “off-target” proteins and immune responses eliciting safety concerns: Comment on UK study by Mulroney et al. ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/376265782_Ribosomal_frameshifting_and_misreading_of_mRNA_in_COVID-19_vaccines_produces_off-target_proteins_and_immune_responses_eliciting_safety_concerns_Comment_on_UK_study_by_Mulroney_et_al
Directed Evolution = Gain of Function
Jordon Trishton Walker. Remember that name from a famous video captured by Project Veritas. Read and comprehend all the implications. Ask yourself why members of the Fifth Column immediately tried to discredit Project Veritas? Directed Evolution is A Thing.






Sucharit Bhakdi, in agony because of what he saw, explained it all, in simple, convincing language, from the very beginning.
Utterly scary and horrific human malevolence! mRNA was touted as a great scientific breakthrough, with the promise of treating intractable diseases like HIV. But when you really think about it for a moment and give it critical light of day thought, you must ask an important and obvious question; how does turning our cells into viral antigens create immunity? Now we know, from ribosomal frame shifting that it causes neo-antigens which alert our complementary surveillance system to tag such cells as foreign viruses. Just disgraceful dystopian science to create disease states for profits.