SNPs increase your Risk of Severe Adverse Reaction to Endotoxin in Jabs
Why do some people react more violently to Endotoxin in Jabs? Let's look at Genetics impact on Epigenetics
Recently my friend and world famous Genomics expert Kevin McKernan reported preliminary findings after incubating Human Ovarian Cancer cells with Pfizer BNT162b2 Lot PB9715 which we know to be made after the company switched from Phosphate Buffer to Tromethamine.
Kevin found SNPs (Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms)1 which means that in copying a DNA sequence, an error occurs by incorporation of the wrong nucleotide in the copy sequence.2
Previously I have emphasized the Epigenetics of Endotoxin poisoning showing the huge upregulation or downregulation of protein expression.3
But that is at a population level. Individuals and certain ethnic minorities often have SNPs that make them more vulnerable to toxic insults.
SNPs increase risk of Thromboembolism and Stroke
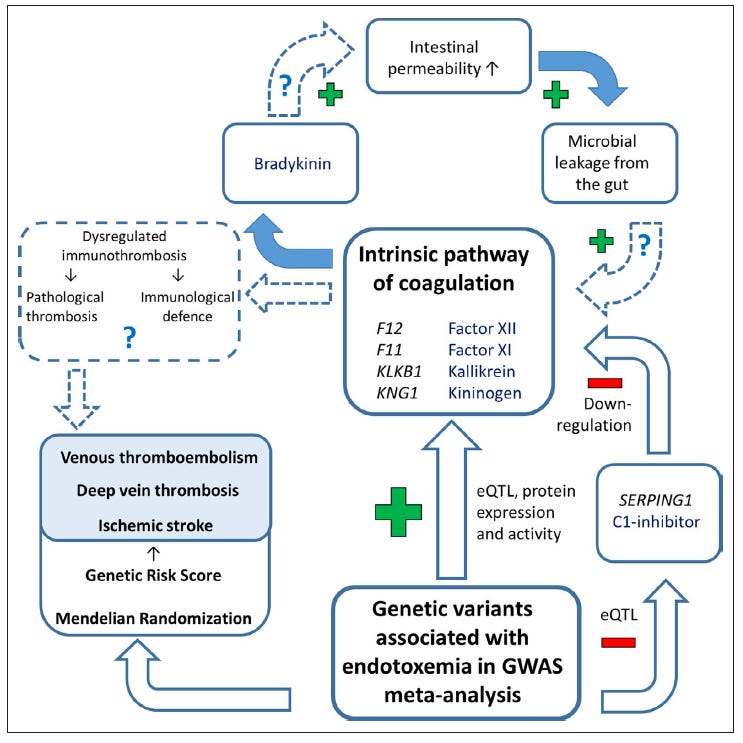
In 2021, researchers examined the serum Endotoxin (Lipopolysaccharide) activity of 11,296 individuals from 6 different Finnish study cohorts4 and reported increased risk of diseases by genome‐wide association. Here is their Figure 3.
At the top we see the familiar fact that a jab in the arm causes a Leaky Gut allowing intrusion of a flood of bacterial Endotoxin in a positive feedback loop.5
Abbreviations in the Figure are: eQTL expression Quantitative Trait Loci; GWAS Genome-Wide Association Study.
The findings included:
Subjects with diabetes have higher serum lipopolysaccharide levels compared with subjects without diabetes because of hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and low HDL cholesterol concentrations.
and increased risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Stroke caused by Endotoxemia.
The study identified a total of 740 markers at five independent loci in Chromosomes 3 (A), 4 (B), 5 (C), 11 (D), and 15 (E) associated with Endotoxemia. Chromosome 12 rs77601517 SNP was found to be of interest only in the FINRISK 1997 cohort and was not studied in detail.
SNPs and Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein
A very useful review by Meng and coworkers6 found associations between many SNPs in the LBP gene on Chromosome 20 and the following diseases but pointed to the need to replicate some small studies:
Increased Predisposition to Sepsis in males (p<0.02) but not in female patients
Infective Endocarditis
3-fold increase in the risk of Death prior to discharge, and a 5-fold increase in Mortality risk after Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.
Atopy and Asthma involving induced CD4+ Th2 differentiation and overproduction of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and related Airway Hyperresponsiveness
Susceptibility to Type 2 Diabetes
HIV-1/HAART-associated Lipodystrophy Syndrome (HALS).
Carotid Intima-Media thickness (CIMT) which is a risk for Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular disease
Atherosclerosis leading to Myocardial Infarction and Stroke
Cancers including Colorectal Carcinoma, Gastric Cancer, Glioma,
Pneumonia and Septic complications
Ovarian Cancer is driven by Endotoxin
Endotoxin is well known to be associated with Ovarian Cancer.7
The reactivity of Ovary cancerous tissue to Endotoxin is greater than normal tissues and stimulation of Ovarian Cancer cells induces Phosphatidyl-Inositol-3 Kinase activation, Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition, and migration marked by the overexpression of N-cadherin, Slug, Vimentin, Snail, α-SMA, TCF, Matrix MetalloProteinase-2 (MMP2), and MMP9.8
Chromosomal variations have been identified in a study of Chinese women with Ovarian Cancer.9 The abstract reads:
Ovarian cancer is one of the most frequent gynecological malignancies worldwide with a poor prognosis. Comparative genomic hybridization has been applied to detect recurrent chromosome alterations in 31 primary ovarian carcinomas in Chinese women. Several nonrandom chromosomal changes were identified including gains of 3q (17 cases, 55%) with a minimum region at 3q25∼q26, 8q (16 cases, 52%), 19q (12 cases, 39%), Xq (11 cases, 35%), 1q (10 cases, 32%), 12p12∼q13 (10 cases, 32%), 17q (10 cases, 32%) with a minimum gain region at 17q21, and 20q (9 cases, 29%); and losses of 16q (9 cases, 29%), 1p (7 cases, 23%), 18q (7 cases, 23%), and 22 (7 cases, 23%). High-copy-number amplification was detected in eleven cases. Amplification of 3q25∼q26 was detected in four cases, and amplifications of 8q24 and 12p11.2∼q12 were observed in three cases each. The recurrent gains and losses of chromosomal regions identified in this study provide candidate regions that may contain oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes involved in the development and progression of ovarian cancer.
Chromosome 9 Toll-like Receptor 4 Endotoxin SNPs
Chromosome 9 Toll-like Receptor 4 Endotoxin SNPs Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile in Ovarian Cancers are associated with tumor progression.10
Chromosome 5 CD14 Endotoxin Binder Polymorphisms and Colorectal Cancer
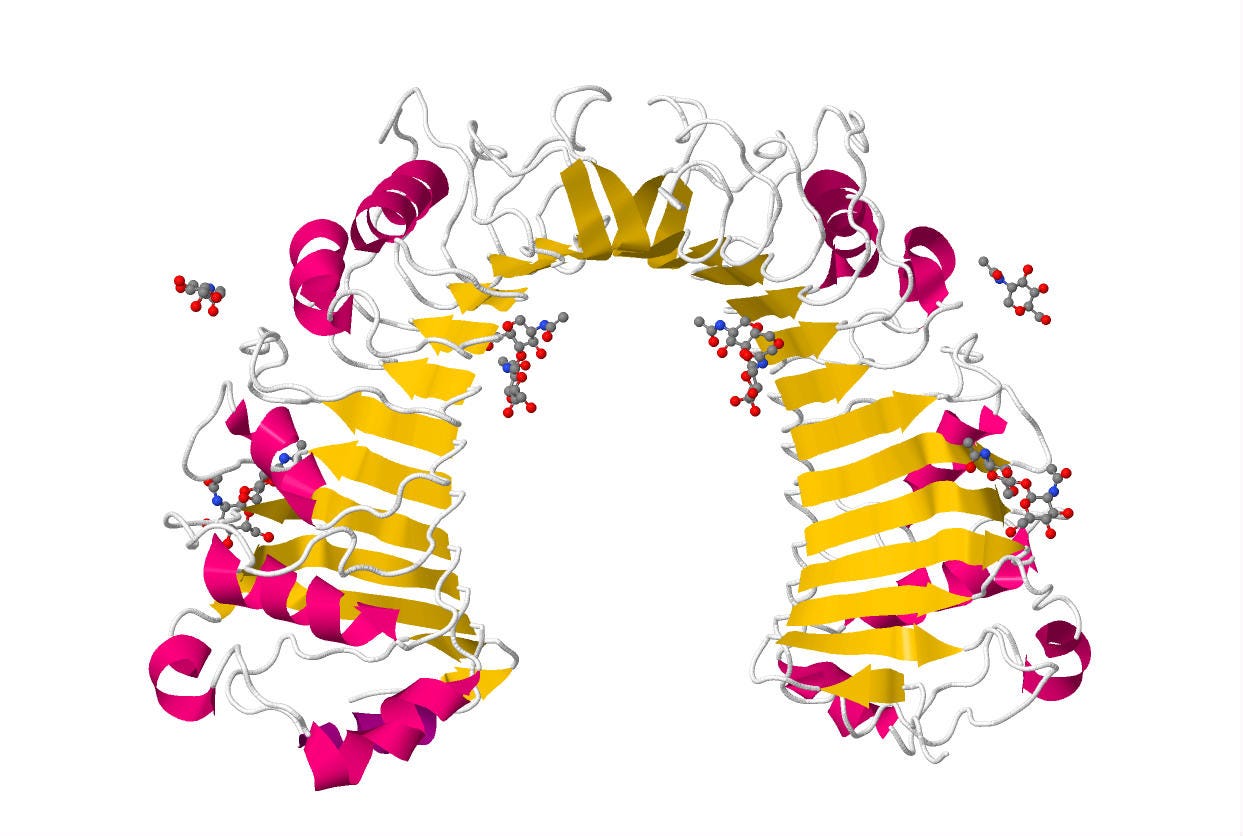
CD14 (Cluster of Differentiation 14) is a human protein that is found bound to the membrane of Human cells and also as a free floating soluble form.11 It binds Endotoxin and is involved in the inflammatory Cytokine Storm. Its crystal structure was solved by Kim and coworkers12 in 2005.
Chinese researchers13 compared Polymorphisms in CD14 were associated with Colorectal Cancer.
SNP on Chromosome 5 CD14 Endotoxin receptor increases risk of Heart Attack
Czech and German scientists found in 1999 that the SNP C(-260)→T nucleotide change in the Promoter region of CD14 is associated with increased risk of Myocardial Infarction.1415
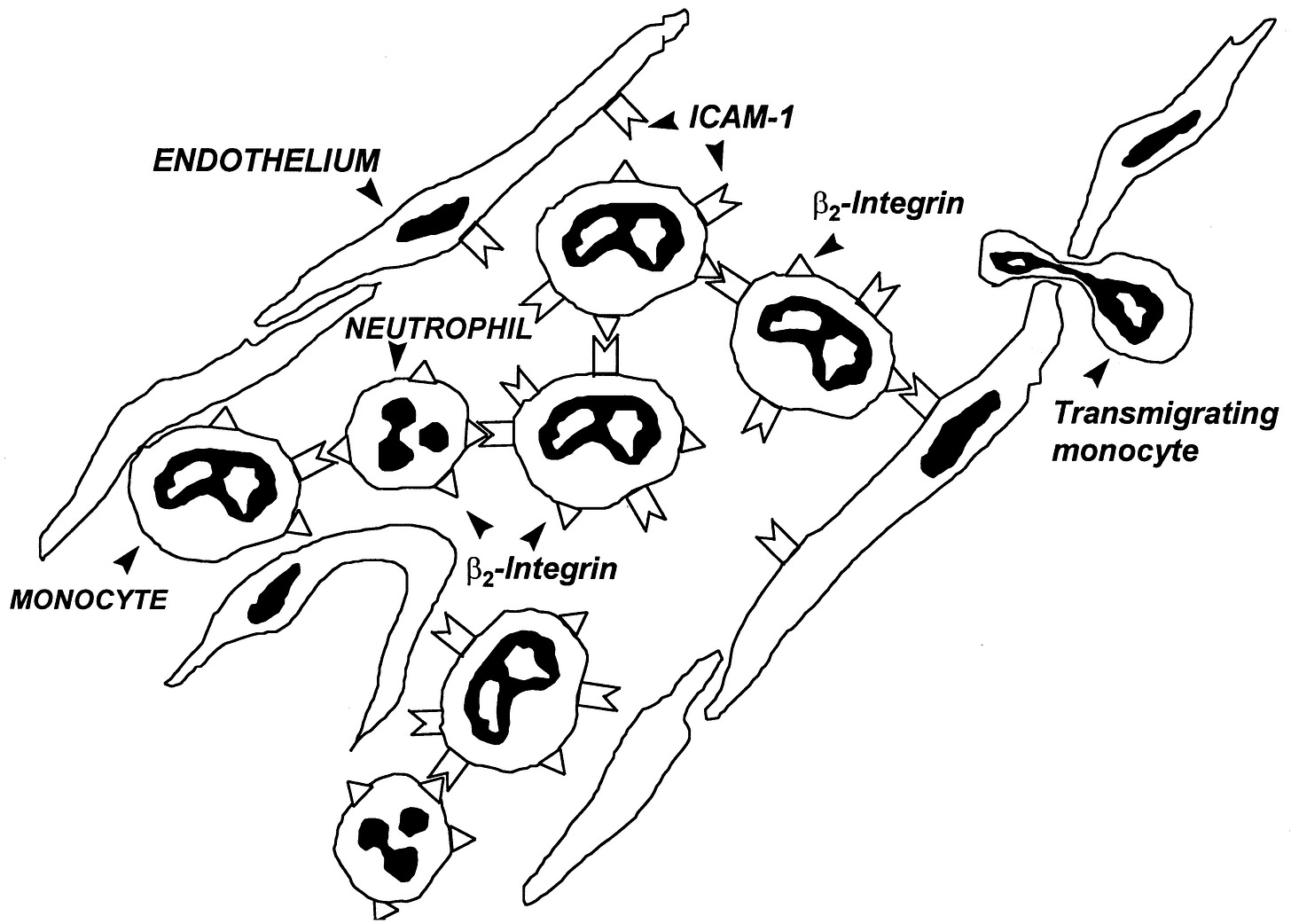
Israeli researchers had earlier found Heart Attack victims had 30% increased CD14 expression.16 They proposed a model for their observations.
Fig. 5. Schematic of possible interaction of activated monocytes with each other or with neutrophils and with altered endothelium. Enhanced expression of ICAM-1 as well as its beta2-integrin ligands LFA-1 and Mac-1 on monocyte cell surface may facilitate their attachment and give rise to aggregate formation. Similarly, monocytes could adhere through the same pathway to altered endothelium that expresses increased ICAM-1 concentration. Both mechanisms could potentially result in microvascular obstruction.
Two SNPs are worse than on in Asthma
Korean researchers17 investigated SNPs in CD14 and Tumor Necrosis Factor related to Asthma and found evidence that the TNF-α promoter polymorphism (−308G/A) might be linked to severe asthma and modulated by the CD14 promoter (−159T/C) polymorphism.
Jab companies fully aware of the problem
An interesting review by Fernando D. Martinez published in 2007, pointed to a number of CD14 polymorphisms known or suspected of causing increased risks to individuals.18 At the time he was on a Merck Advisory Board and acted as a consultant for Genentech and Pfizer.
Sensors to detect SNPs
Thanks to Ronnette Erwin of Substack who pointed me to Endotoxin induced miRNA-21 developments, including a biosensor that can detect Femtomolar amounts of it and even individual SNPs in the miR-21.19 Perhaps this technology will be applied to studies of integration of synthetic DNA from jabs into the Human Genome.
As usual, I will add more references as they are found.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single-nucleotide_polymorphism
Epigenetics of Endotoxin Poisoning from Pfizer Jabs
Jaakko Leskelä et al. 2021. Genetic Profile of Endotoxemia Reveals an Association With Thromboembolism and Stroke. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/355462660_Genetic_Profile_of_Endotoxemia_Reveals_an_Association_With_Thromboembolism_and_Stroke
Leilei Meng, Zichen Song, Anding Liu, Uta Dahmen, Xiao Yang and Haoshu Fang. 2021. Effects of Lipopolysaccharide- Binding Protein (LBP) Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) in Infections, Inflammatory Diseases, Metabolic Disorders and Cancers. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.681810/full
Adrienn Sipos, Gyula Ujlaki, Edit Mikó, Eszter Maka, Judit Szabó, Karen Uray, Zoárd Krasznai and Péter Bai. 2021. The role of the microbiome in ovarian cancer: mechanistic insights into oncobiosis and to bacterial metabolite signaling. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8017782/
Ga Bin Park, Yoon Hee Chung and Daejin Kim. 2017. Induction of galectin-1 by TLR-dependent PI3K activation enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition of metastatic ovarian cancer cells. https://www.spandidos-publications.com/or/37/5/3137
Jonathan S T Sham, Terence C-M Tang, Yan Fang, Li Sun, Lun-Xiu Qin, Qiu-Liang Wu, Dan Xie, Xin-Yuan Guan. 2002. Recurrent chromosome alterations in primary ovarian carcinoma in Chinese women. https://www.cancergeneticsjournal.org/article/S0165-4608(01)00567-2/abstract
AN-CONG WANG, FENG-XIA WU, YONG-SHENG GAO, and XIU-GUI SHENG. Toll-like receptor 4 single-nucleotide polymorphisms Asp299Gly and Thr399Ile in ovarian cancers. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4063650/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CD14
Kim JI, Lee CJ, Jin MS, Lee CH, Paik SG, Lee H, Lee JO (2005). Crystal structure of CD14 and its implications for lipopolysaccharide signaling. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021925820808357
Qiusha Guo, Jianbo Zhu and Bing Xia. 2006. Polymorphism of CD14 gene but not the mutation of TLR4 gene is associated with colorectal cancer in Chinese patients. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2005.04156.x
Jaroslav A. Hubacek, Gregor Rothe, Jan Pit’ha, Zdena S̆kodová, Vladimír Stanĕk, Rudolf Poledne, Gerd Schmitz. 1999. C(-260)→ T Polymorphism in the Promoter of the CD14 Monocyte Receptor Gene as a Risk Factor for Myocardial Infarction. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.100.25.2550
Jaroslav A. Hubacek, Jan Pit’ha, Zdena Škodová, Vladimír Stanĕk and Rudolf Poledne. 1999. C(-260)→ T Polymorphism in the Promoter of the CD14 Monocyte Receptor Gene as a Risk Factor for Myocardial Infarction. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/01.CIR.99.25.3218
SIMCHA R. MEISEL, HAVA SHAPIRO, JUDITH RADNAY, YORAM NEUMAN, ABDUL-RAHIM KHASKIA, NACHMAN GRUENER, HANA PAUZNER and DANIEL DAVID. Increased Expression of Neutrophil and Monocyte Adhesion Molecules LFA-1 and Mac-1 and Their Ligand ICAM-1 and VLA-4 Throughout the Acute Phase of Myocardial Infarction: Possible Implications for Leukocyte Aggregation and Microvascular Plugging. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0735109797004245
Soo-Jong Hong 1 , Hyo-Bin Kim, Mi-Jin Kang, So-Yeon Lee, Ja-Hyung Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Seong-Ok Jang, Hyung-Doo Shin, Choon-Sik Park. 2007. TNF-alpha (-308 G/A) and CD14 (-159T/C) polymorphisms in the bronchial responsiveness of Korean children with asthma. https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(06)02299-8/fulltext
Fernando D. Martinez 2007. CD14, Endotoxin, and Asthma Risk Actions and Interactions. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2647622/
Ya Wang, Mengyao Li and Yuzhong Zhang. 2021. Electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 based on a Au nanoparticle functionalized g-C3N4 nanosheet nanohybrid as a sensing platform and a hybridization chain reaction amplification strategy. https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2021/an/d1an00029b



Here’s that paper on Chimeric RNAs as a transcriptional network on Chromosomes 20 and 21. https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0028213 It would be useful to look at discarded microbiome chimeras from published data sets. And Dr Sabine Hazan has before and after shot samples.