TENT5 - chasing Poly A Tails while ignoring the Endotoxin upregulation
Much excitement in some quarters by the final publication of a revised preprint by Pawel S Krawczyk et al. enthusiastically investigating Re-Adenylation after Jabbing with Moderna Covid19 shot
Why do many in the Genomic Sequencing community ignore the fundamental Endotoxin research by the Polish scientists that led them to the latest paper?
But first let’s look at the Jab Developer frightening discovery that contradicts mRNA Jab manufacturer statements about which Human Cells are the primary target of the LNPs carrying the GMO poison.
Here is the lead author announcement from 17 April 2025.
Link to the TENT5A paper in Nature. Impressive list of authors, and following European academic tradition, the head researchers in the laboratories receiving correspondence are listed last.1
You can follow Pawel on X where he created a thread for discussion.2
Here Pawel describes the result of the team research and his own breakthrough.
I have removed some emojis and #tag links, but have provided the publications referenced:
Incredibly proud to share my first-author paper in @Nature! Heartfelt thanks to my mentor @AndrzejDziembo1 and the brilliant team at @DziembowskiLab
Our research elucidates a critical post-transcriptional modification enhancing #mRNA #vaccine efficacy. We've identified #TENT5A-mediated re-adenylation as a key determinant of therapeutic mRNA stability and immunogenicity in #SARS_CoV_2 #vaccines. #mRNABiology
We employed @nanopore #direct #RNA #sequencing (DRS) to characterize individual therapeutic mRNA molecules - specifically focusing on #polyA #tail dynamics. However, #methylpseudouridine (mΨ) modifications in therapeutic mRNAs create significant analytical challenges.
To overcome this obstacle, I developed a Dynamic Time Warping approach to detect and analyze vaccine molecules using #DRS with high fidelity, enabling precise characterization of #polyA tails from #therapeutic #mRNAs.
The @moderna_tx #mRNA-1273 vaccine possesses a ~100 nucleotide #polyA tail terminated with a distinctive pentamer (mΨCmΨAG), which served as a critical molecular marker, facilitating differentiation between processed and unprocessed tails.
In typical cellular models (HEK293T), we observed that mRNA-1273 degradation is initiated via removal of the terminal pentamer (mΨCmΨAG), followed by #CCR4-NOT-mediated #deadenylation - the canonical #mRNA #decay pathway. #RNAMetabolism
Crucially, when examining #mRNA #vaccines at injection sites in #mice, we discovered an unexpected phenomenon: #polyA tails were extended from ~100 to ~200 nucleotides - contradicting the expected degradation pattern observed in standard cell lines. #mRNAStability
We then detected the same #polyA elongation pattern in #macrophages - both those sorted from muscles surrounding injection sites and in the in vitro models (mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (mBMDMs) and human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDMs).
We identified #TENT5A -a polyA polymerase our lab has studied extensively - as responsible for this effect. Its expression is induced by vaccine delivery, most likely through innate immune signaling (please compare our previous paper).3
Of note, recent work from our lab by @nemitheasura showed that TENT5A incorporates non-adenosines into poly(A) tails of mRNA-1273, further underscoring its role in shaping the fate of therapeutic mRNAs.4
We found that #macrophages- not dendritic cells- are the primary cells that take up mRNA vaccine #LNPs and express #TENT5A, positioning them as key players in regulating mRNA stability via re-adenylation.
The re-adenylation phenomenon exhibits substrate specificity - consistently observed in synthetic mRNAs encoding proteins targeted to the #endoplasmic #reticulum (ER), including #spike #glycoprotein, #Zika virus antigens, and #malaria parasitic proteins.
Surprisingly, comparative analysis revealed differential re-adenylation efficiency between vaccine formulations:
@BioNTech_Group - @pfizer
#BNT162b2 demonstrated reduced re-adenylation compared to mRNA-1273, correlating with diminished #ER membrane association.
Our findings reveal a mechanistic principle: spatial proximity to ER-resident #TENT5A governs re-adenylation efficiency.
This positions the #endoplasmic #reticulum as a central hub not only for #mRNA translation, but also for post-transcriptional regulation.
Mouse in vivo studies showed that TENT5A-deficient mice produced significantly less antigen-specific #antibodies following #mRNA#vaccination. This highlights the essential role of #TENT5A in mounting an effective immune response to mRNA-based vaccines.
Notably, this effect was specific to #mRNA vaccines - #TENT5A deficiency did not impair antibody production in response to the protein-based #vaccine #Nuvaxovid @Novavax.
These findings have immediate implications for therapeutic mRNA design: optimization of ER-targeting signals could enhance TENT5A-mediated re-adenylation, potentially improving vaccine efficacy and reducing dosage requirements.
This publication represents the culmination of a long,challenging journey.
We initially posted our findings as a #preprint on @biorxivpreprint in December 2022. The rigorous review process demanded additional experiments, which significantly strengthened our final manuscript.
Notably, this represents a landmark achievement as likely the first @Nature article of the 21st century conducted entirely in #Polish laboratories!
Huge thanks to everyone involved—our incredible team - @DziembowskiLab , collaborators @UniWarszawski #WUM, @IBBPAS and funding agencies -
@ERC_Research, @NCN_PL, @FNP_org_pl, @PORT_Wroclaw .
I'm grateful for this milestone in my career - an experience that’s shaped me both scientifically and personally. Looking ahead with excitement to the next chapter and new opportunities to grow.
Change of Paper Title
One point of interest is that the paper title changed between the 2022 preprint and the final Nature version with increased number of authors. The preprint had 2 published versions posted on 1 December 2002 and 16 December 2022.56
Endotoxin TENT5 paper in November 2022
There was considerable discussion on Twitter (now X) at the time, about Reference 3 mentioned in the quoted Pawel thread above, but unfortunately I was thrown off that platform at that time and was about to discover Gettr.
Here is his announcement of the paper published in Science that I find most interesting:
The Abstract:
Innate immunity is the first line of host defense against pathogens.
Here, through global transcriptome and proteome analyses, we uncover that newly described cytoplasmic poly(A) polymerase TENT-5 (terminal nucleotidyltransferase 5) enhances the expression of secreted innate immunity effector proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Direct RNA sequencing revealed that multiple mRNAs with signal peptide–encoding sequences have shorter poly(A) tails in tent-5–deficient worms.
Those mRNAs are translated at the endoplasmic reticulum where a fraction of TENT-5 is present, implying that they represent its direct substrates.
Loss of tent-5 makes worms more susceptible to bacterial infection.
Notably, the role of TENT-5 in innate immunity is evolutionarily conserved.
Its orthologs, TENT5A and TENT5C, are expressed in macrophages and induced during their activation.
Analysis of macrophages devoid of TENT5A/C revealed their role in the regulation of secreted proteins involved in defense response.
In summary, our study reveals cytoplasmic polyadenylation to be a previously unknown component of the posttranscriptional regulation of innate immunity in animals.
The body of the text is of very great interest to me and I list the prior publications cited below.
The role of TENT-5 in innate immunity is evolutionarily conserved
Because TENT-5 is orthologous to mammalian TENT5 ncPAPs, we hypothesized that mammalian TENT5 proteins might also have a role in innate immunity. Murine macrophages, key innate immune effector cells, express two of the four Tent5 genes, Tent5a and Tent5c.
We found that both genes were induced in bone marrow–derived macrophages (BMDMs) upon stimulation with LipoPolySaccharide (LPS, Endotoxin), which is a potent activator of inflammatory and immune response in M1 macrophages (Fig. 7A) (68).7
To test whether TENT5A and TENT5C proteins also were activated during infection, we examined their levels in the time course of LPS treatment in BMDM isolated from TENT5A-3xFLAG (26)8 and TENT5C-3xFLAG knockin mouse lines (21) - see my reference 10 below.
The effectiveness of BMDM activation was examined by analysis of M1 macrophage polarization markers inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and CD80 (Fig. 7B) (69).9
Similarly, TENT5A-3xFLAG and TENT5C-3xFLAG levels were elevated in response to LPS stimulation (Fig. 7B), consistent with the notion that the role of TENT5 ncPAPs in innate immunity could be evolutionarily conserved.
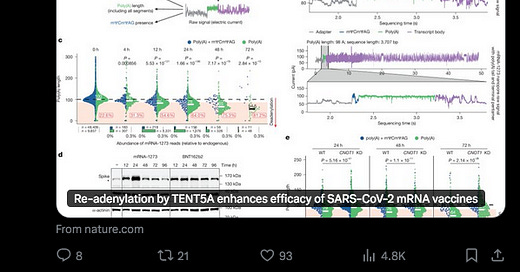
Here is their Figure 7 showing the effects of Endotoxin (LPS) on TENT5 expression on 98 microRNAs. Please click to enlarge.
The caption is very detailed:
Fig. 7. The role of TENT-5 in innate immunity is evolutionarily conserved.
(A) Heatmap showing expression levels of Tent5 genes in BMDMs isolated from the wild-type mice.
Stimulation of BMDMs with LPS led to increased expression levels of Tent5a/c.
(B) TENT5A/C were elevated in macrophages stimulated with LPS as illustrated by anti-FLAG immunoblots on extracts prepared from wild-type (WT), TENT5A-3xFLAG (AF), and TENT5C-3xFLAG (CF) BMDMs.
iNOS and CD80 levels serve as a control of BMDM activation. The lines and asterisks indicate specific and unspecific bands, respectively.
(C) Plot showing expression levels and difference in the median poly(A) tail length of mRNAs that were isolated from Tent5a−/− Tent5c−/− and wild-type BMDMs. TENT5A/C-regulated transcripts (n = 98) are marked in red (FDR < 0.05).
(D) Top 20 (ordered by adjusted P value) GO terms of TENT5A/C substrate mRNAs (data S6).
(E) Bee swarm plots of poly(A) tail length distributions for the top 20 TENT5A/C molecular substrates ordered by the median poly(A) tail length fold change (data S6).
(F) Western blots showing that the lack of TENT5A/C leads to the lower abundance of indicated peptides both in unstimulated (LPS; 0 hours) and stimulated (LPS; 8 hours) BMDMs.
Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) serves as a loading control. Shown is the representative result of three biological replicates (fig. S7K).
Graphs on the right show values of the band intensity ratio between tested protein and GAPDH. Points indicate values of each of three biological replicates, and lines denote the average value for biological replicas. *P ≤ 0.05 (two-tailed t test).
The text goes on at great length to discuss everything in Figure 7, and luckily we can read it free of charge.
Attacks were launched in December 2022 on the Polish Group by an irritating German, using an alias, “AGenervt” who had his account suspended and has banned me for life from commenting on his Substack articles. His expression “Narf!” might prompt some readers’ memories.
Here is Pawel Krawczyk’s restrained and polite response to him in the thread.
Cancer Consequences
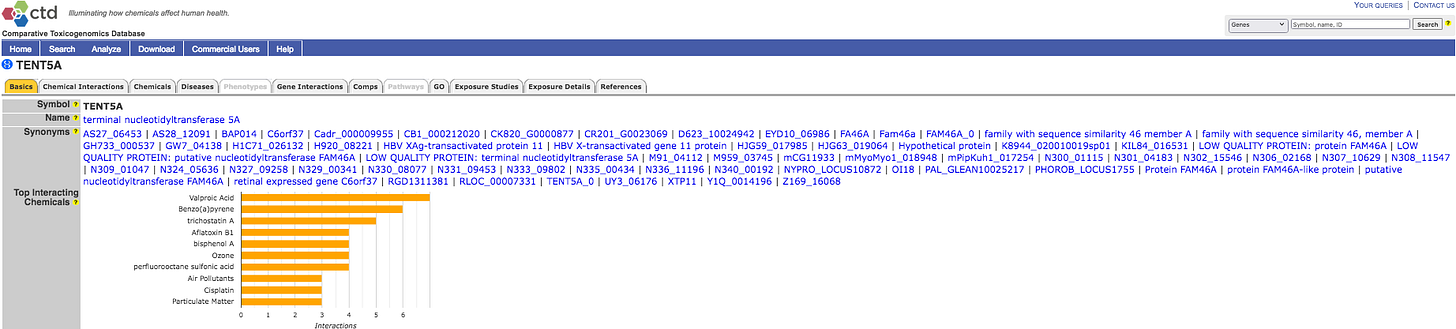
When studying the wider Jab induced effects of altering TENT5 expression, it is necessary to look at Synonyms, for example FAM46C.
The US Government Comparative Toxicogenomics Database might not have had enough Human Curation, but does list many references for further study.
Please click to expand and note some top chemicals that affect the gene.
In the Nature paper (reference 1 below) we see this research group citing another of their earlier studies.10
Abstract
FAM46C is one of the most frequently mutated genes in multiple myeloma.
Here, using a combination of in vitro and in vivo approaches, we demonstrate that FAM46C encodes an active non-canonical poly(A) polymerase which enhances mRNA stability and gene expression.
Reintroduction of active FAM46C into multiple myeloma cell lines, but not its catalytically-inactive mutant, leads to broad polyadenylation and stabilization of mRNAs strongly enriched with those encoding endoplasmic reticulum-targeted proteins and induces cell death.
Moreover, silencing of FAM46C in multiple myeloma cells expressing WT protein enhance cell proliferation.
Finally, using a FAM46C-FLAG knock-in mouse strain, we show that the FAM46C protein is strongly induced during activation of primary splenocytes and that B lymphocytes isolated from newly generated FAM46C KO mice proliferate faster than those isolated from their WT littermates.
Concluding, our data clearly indicate that FAM46C works as an onco-suppressor, with the specificity for B-lymphocyte lineage from which multiple myeloma originates.
FAM46C is one of the most frequently mutated genes in multiple myeloma (MM), but its molecular function remains unknown.
Here the authors show that FAM46C is a poly(A) polymerase and that loss of function of FAM46C drives multiple myeloma through the destabilisation of ER response transcripts.
In that paper they used Endotoxin to induce activation of the Primary Splenocytes.
How do the mRNA Jabs mutate TENT5 = FAM46C and related proteins?
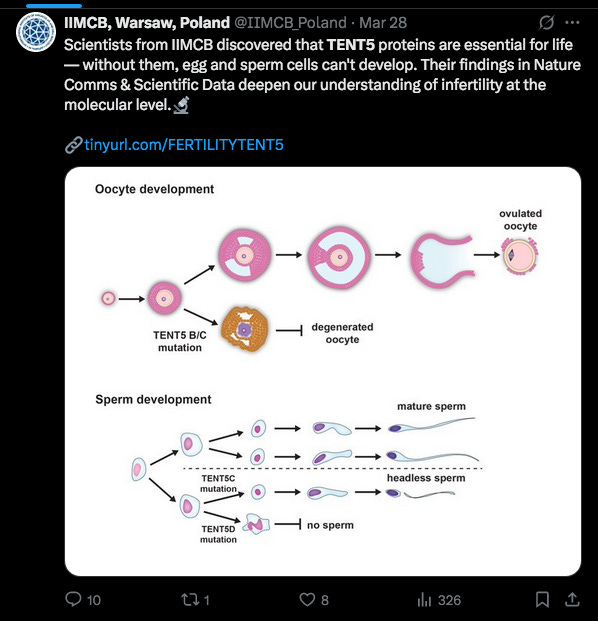
Infertility and Birth Defects
The Polish researchers are helping us Jab resisters with a flurry of new papers.
Here is an announcement on 28 March 2025 talking about the role of TENT5 on Sperm and Egg development, with a link to a recent paper, expanding on an earlier one in 2024.11
Short Message
Endotoxin alone is responsible for upregulation of TENT5 which results in Poly A Tail extension observed in Moderna mRNA Jabbing.
I note there are a number of publications in languages other than english, but have not had time to look.
See also commentary by Maria Gutschi12 .
Please share and gather comments.
Paweł S. Krawczyk, Michał Mazur, Wiktoria Orzeł, Olga Gewartowska, Sebastian Jeleń, Wiktor Antczak, Karolina Kasztelan, Aleksandra Brouze, Katarzyna Matylla-Kulińska, Natalia Gumińska, Bartosz Tarkowski, Ewelina P. Owczarek, Kamila Affek, Paweł Turowski, Agnieszka Tudek, Małgorzata Sroka, Tomasz Śpiewla, Monika Kusio-Kobiałka, Aleksandra Wesołowska, Dominika Nowis, Jakub Golab, Joanna Kowalska, Jacek Jemielity, Andrzej Dziembowski, Seweryn Mroczek. 2025. Re-adenylation by TENT5A enhances efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines.
https://x.com/pakraw
Vladyslava Liudkovska, Paweł S. Krawczyk, Aleksandra Brouze, Natalia Gumińska, Tomasz Wegierski, Dominik Cysewski, Zuzanna Mackiewicz, Jonathan J. Ewbank, Krzysztof Drabikowski, Seweryn Mroczek, and Andrzej Dziembowski. 2022. TENT5 cytoplasmic noncanonical poly(A) polymerases regulate the innate immune response in animals. https://www.science.org/doi/full/10.1126/sciadv.add9468
Natalia Gumińska, Katarzyna Matylla-Kulińska, Paweł S. Krawczyk, Michał Maj, Wiktoria Orzeł, Zuzanna Mackiewicz, Aleksandra Brouze, Seweryn Mroczek & Andrzej Dziembowski. 2025. Direct profiling of non-adenosines in poly(A) tails of endogenous and therapeutic mRNAs with Ninetails. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-57787-6
Paweł S Krawczyk, Olga Gewartowska, Michał Mazur, Wiktoria Orzeł, Katarzyna Matylla-Kulińska, Sebastian Jeleń, Paweł Turowski, Tomasz Śpiewla, Bartosz Tarkowski, Agnieszka Tudek, Aleksandra Brouze, Aleksandra Wesołowska, Dominika Nowis, Jakub Gołąb, Joanna Kowalska, Jacek Jemielity, Andrzej Dziembowski, and Seweryn Mroczek. 1 December 2022. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine is re-adenylated in vivo, enhancing 1 antigen production and immune response.
Paweł S Krawczyk, Olga Gewartowska, Michał Mazur, Wiktoria Orzeł, Katarzyna Matylla-Kulińska, Sebastian Jeleń, Paweł Turowski, Tomasz Śpiewla, Bartosz Tarkowski, Agnieszka Tudek, Aleksandra Brouze, Aleksandra Wesołowska, Dominika Nowis, Jakub Gołąb, Joanna Kowalska, Jacek Jemielity, Andrzej Dziembowski, and Seweryn Mroczek. 16 December 2022. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine is re-adenylated in vivo, enhancing antigen production and immune response.
P. J. Murray, Macrophage polarization. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 79:541–566
O. Gewartowska, G. Aranaz-Novaliches, P. S. Krawczyk, S. Mroczek, M. Kusio-Kobiałka, B. Tarkowski, F. Spoutil, O. Benada, O. Kofroňová, P. Szwedziak, D. Cysewski, J. Gruchota, M. Szpila, A. Chlebowski, R. Sedlacek, J. Prochazka, A. Dziembowski. 2021. Cytoplasmic polyadenylation by TENT5A is required for proper bone formation. Cell Rep. 35:109015.
M. Benoit, B. Desnues, J.-L. Mege. 20028. Macrophage polarization in bacterial infections. J. Immunol. 181:3733–3739
Seweryn Mroczek, Justyna Chlebowska, Tomasz M Kuliński, Olga Gewartowska, Jakub Gruchota, Dominik Cysewski, Vladyslava Liudkovska, Ewa Borsuk, Dominika Nowis, Andrzej Dziembowski. 2017. The non-canonical poly(A) polymerase FAM46C acts as an onco-suppressor in multiple myeloma.
Michał Brouze, Agnieszka Czarnocka-Cieciura, Olga Gewartowska, Monika Kusio-Kobiałka, Kamil Jachacy, Marcin Szpila, Bartosz Tarkowski, Jakub Gruchota, Paweł Krawczyk, Seweryn Mroczek, Ewa Borsuk & Andrzej Dziembowski. 2024. TENT5-mediated polyadenylation of mRNAs encoding secreted proteins is essential for gametogenesis in mice.




Oh, great. More bad news.