siRNA used to study Endotoxin Poisoning
Short Interfering RNA is in the news, so let's see how it has been used to study details of Jab Endotoxin harms
I do hope people work to stop the mass injection of siRNA (Short Interfering RNA) Lipid Nanoparticles designed to transfect every cell type in the human body.
But siRNA has been widely used in laboratory experiments at cellular level in vitro and with test animals in vivo to “knock down” or Genetically Modify cells to study details of molecular pathways. Here the focus is on Endotoxin.
HIV Persistence and Dissemination caused by Endotoxin
siRNA was used in knock out experiments to investigate how Endotoxin contributes to ongoing HIV infection as reviewed by researchers in France.1
The capation reads:
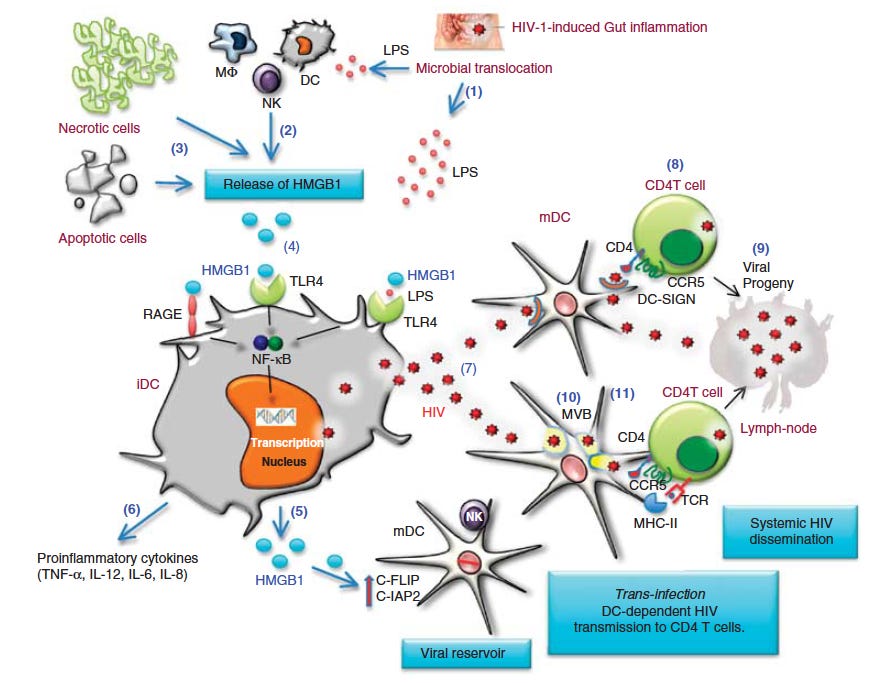
Figure 6 Proposed contribution of HMGB1 to HIV persistence and dissemination. HIV disease progression is characterized by gut inflammation and consequently microbial translocation leading to the release of LPS (Endotoxin) in the bloodstream (1).
Circulating LPS may induce active release of HMGB1 by innate cells, including macrophages and DCs (2). Necrotic and apoptotic cells that accumulate during chronic HIV infection may also be a constant source of HMGB1 (3). HMGB1 activates DCs by signaling through the receptor RAGE or TLR4 if cooperate with TLR4 ligand LPS, thus triggering NF-kB activation (4). This results in the release of HMGB1 (5) and proinflammatory cytokines (6), and the triggering of HIV replication in mDCs (7). Trans-infection of HIV from mDCs to CD4 T cells involves HIV capture by DC-SIGN followed by its recruitment at the site of T-cell interaction (8). This infectious synapse will lead to the productive infection of CD4 T cells (9). Trans-infection of HIV can also be mediated by exocytosis of the HIV-1 particles captured by DCs. After endocytosis, the captured HIV-1 particles are targeted to a multi-vesicular endosomal body (MVB) in DCs (10). Although some of the MVB-localized virus fraction is targeted to the lysosome and degraded to be further presented to TCR in the context of MHC molecules, fusion of MVB with the plasma membrane results in the release of virus particles along with exosomes (11). Virus produced by infected CD4 T cells, DCs and macrophages spread the infection to the draining lymph nodes and other lymphoid tissue
Capillary Leak in Toxic Shock
siRNA was used by researchers from Austria, Russia and UK to investigate the frequently fatal Capillary Leak caused by endothelial attack in Toxic Shock induced by Viruses and Endotoxin.2
Hydrogen Sulfide Gasotransmitter
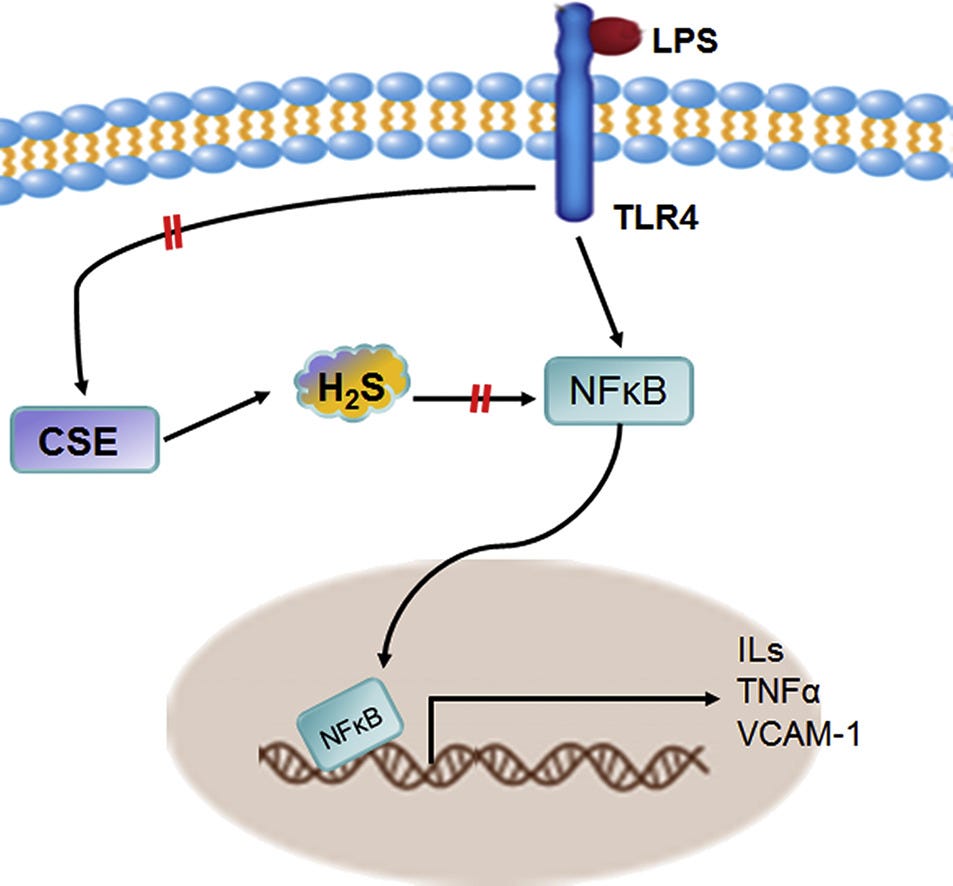
siRNA was used by researchers in Canada and China to knock out the TLR4 Endotoxin receptor to study cross talk between Endotoxin-induced inflammation and the Cystathionine gamma-lyase Enzyme (CSE)/H2S system in vascular cells.3
They showed Endotoxin caused hyper-permeability of cells.
The possible mechanism underlying H2S-protected inflammation development and hype r-permeability by LPS. LPS stimulates the transactivation of transcription factor NFκB by activating TLR4, which then promotes the transcription of inflammation-related genes following increased cytokine secretion. LPS reduces CSE/H2S signalling and enhancement of CSE/H2S system would protect the detrimental effect of LPS in vascular system.
Necrotic Cell Death caused by Endotoxin
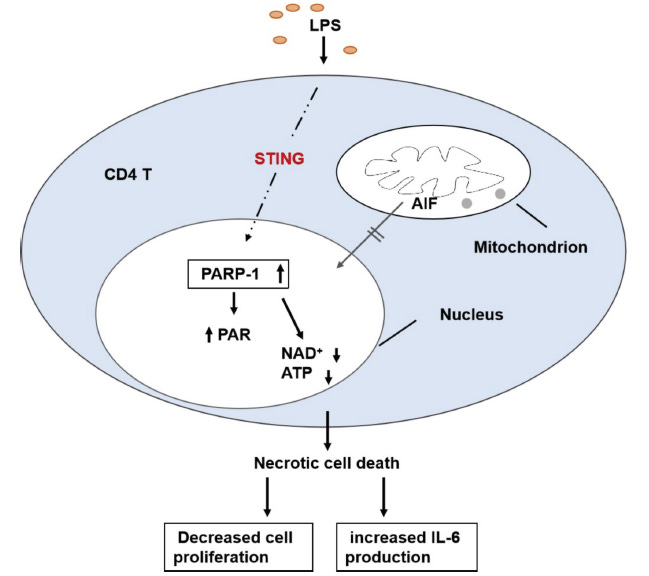
In 2022 researchers in China4 used siRNA to knock out Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1 (PARP-1) activity in Necrotic Cell Death of CD4 T cells stimulated by Endotoxin showing the cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase-Stimulator of Interferon Genes (cGAS-STING) pathway to depends on PARP-1.
Fig. 6. Proposed mechanism of STING modulated Necrotic Death in CD4 T cell. STING acting through activation of PARP-1 in CD4 T cells triggers accumulations of PAR polymer and depletion of ATP and NAD+, which in turn initiates a cascade of cellular and molecular events. AIF did not participate in the execution of necrotic cell death mediated by STING in CD4 T cells
Note they found that Apoptosis-Inducing Factor (AIF) from mitochondria was not required for Endotoxin induced cell death.
M-L Gougeon, M-T Melki and H Saıdi. 2012. HMGB1, an alarmin promoting HIV dissemination and latency in dendritic cells. Cell Death and Differentiation 19, 96–106
Marion Groger, Waltraud Pasteiner, George Ignatyev, Ulrich Matt, Sylvia Knapp, Alena Atrasheuskaya, Eugenij Bukin, Peter Friedl, Daniela Zinkl, Renate Hofer-Warbinek, Kai Zacharowski, Peter Petzelbauer, Sonja Reingruber. 2009. Peptide Bβ15-42 Preserves Endothelial Barrier Function in Shock. PLoS ONE 4(4): e5391
Caitlyn Bourque, Yanjie Zhang, Ming Fu, Mélanie Racine, Adam Greasley, Yanxi Pei, Lingyun Wu, Rui Wang, Guangdong Yang. 2017. H2S protects lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation by blocking NFκB transactivation in endothelial cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2017.11.004 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0041008X17304416
Ying-yi Luan, Lei Zhang, Yi-qiu Peng, Ying-ying Li, Cheng-hong Yin. 2022. STING modulates necrotic cell death in CD4 T cells via activation of PARP-1/PAR following acute systemic inflammation. International Immunopharmacology 109:108809