Fluoridation Industrial Waste Disposal Causes Immunodeficiency
While we wait for Justice Edward Chen to decide whether to compel the USEPA to use their Power to Ban Fluoridation across USA, time to revisit my old Questions
Prompted by recent Robert Malone Friday Funnies meme sharing, I dug out this Ben Garrison creation from the time when they were called Cartoons.
His ability to get to the heart of a vital matter is exceptional, as in this one on Fauci.
Now back to the topic that will require expansion after sharing a first pass.
On 4 February 2020 I asked1 the ResearchGate Community a Question:
Then in July 2021 I followed up2 after more research with another Question:
Ten years earlier I had a grounding in Somatic Hypermutation3 in generation of Immunity when I worked in a Genetics Lab.
Through my research into Fluoride Toxicology, I had discovered the US Government Comparative Toxicogenomics Database houses a huge resource and in particular, at the time, it linked Fluoride with Immunodeficiency via ACP5 AK2 C8B CD36 CD3E CD3G CD40LG IL2 LAMTOR2 MSN NFKBIA PGM3 PLCG2 STAT2 STK4 STIM1 Genes. So I will list these genes as subheadings and return later to add information, using information from the US National Library of Medicine as starters.
ACP5
ACP5 gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase type 5 (TRAP). This has an Iron atom in the active site.
AK2
AK2 gene encodes the mitochondrial energy metabolism enzyme adenylate kinase 2 (AK2).
C8B
C8B gene encodes one of the three subunits of the complement component 8 (C8) protein.
CD36
CD36 encodes a major glycoprotein of the platelet surface and serves as a receptor for thrombospondin in platelets and various cell lines.
CD3E
CD3 epsilon gene encodes the CD3-epsilon polypeptide, which together with CD3-gamma, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex. This complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways.
CD3G
CD3G gene encodes CD3-gamma polypeptide, which together with CD3-epsilon, -delta and -zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T-cell receptor-CD3 complex.
CD40LG
CD40 ligand gene encodes protein expressed on the surface of T cells. It regulates B cell function by engaging CD40 on the B cell surface.
IL2
Interleukin 2 gene encodes protein that is a secreted cytokine produced by activated CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, that is important for the proliferation of T and B lymphocytes.
LAMTOR2
Late endosomal/lysosomal adaptor, MAPK and MTOR activator 2 gene encodes protein associated with the cytoplasmic face of late endosomes and lysosomes. The mouse protein interacts with MAPK scaffold protein 1, a component of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. In humans, a mutation in this gene has been associated with a primary immunodeficiency syndrome.
MSN
Moesin (Membrane-Organizing Extension Spike Protein) is thought to function as cross-linkers between plasma membranes and actin-based cytoskeletons. Moesin is localized to filopodia and other membranous protrusions that are important for cell-cell recognition and signaling and for cell movement.
NFKBIA
NFKB inhibitor alpha gene encodes a member of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor family, which contain multiple ankrin repeat domains. The encoded protein interacts with REL dimers to inhibit NF-kappa-B/REL complexes which are involved in inflammatory responses. The encoded protein moves between the cytoplasm and the nucleus via a nuclear localization signal and CRM1-mediated nuclear export.
PGM3
PhosphoGlucoMutase 3 gene encodes a member of the phosphohexose mutase family. The encoded protein mediates both glycogen formation and utilization by catalyzing the interconversion of glucose-1-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate.
PLCG2
Phospholipase C Gamma 2 gene encodes a transmembrane signaling enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1-phosphatidyl-1D-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate to 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) using calcium as a cofactor. IP3 and DAG are second messenger molecules important for transmitting signals from growth factor receptors and immune system receptors across the cell membrane.
STAT2
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 2 gene encodes proteins that are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. In response to interferon (IFN), this protein forms a complex with STAT1 and IFN regulatory factor family protein p48 (ISGF3G), in which this protein acts as a transactivator, but lacks the ability to bind DNA directly. The protein mediates innate antiviral activity.
STK4
Serine/Threonine Kinase 4 gene encodes a cytoplasmic kinase that is structurally similar to the yeast Ste20p kinase, which acts upstream of the stress-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. The encoded protein can phosphorylate myelin basic protein and undergoes autophosphorylation. A caspase-cleaved fragment of the encoded protein has been shown to be capable of phosphorylating histone H2B. The particular phosphorylation catalyzed by this protein has been correlated with apoptosis, and it's possible that this protein induces the chromatin condensation observed in this process.
STIM1
Stromal Interaction Molecule 1 gene encodes a type 1 transmembrane protein that mediates Ca2+ influx after depletion of intracellular Ca2+ stores by gating of store-operated Ca2+ influx channels (SOCs). It is one of several genes located in the imprinted gene domain of 11p15.5, an important tumor-suppressor gene region. Alterations in this region have been associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, adrenocrotical carcinoma, and lung, ovarian, and breast cancer. This gene may play a role in malignancies and disease that involve this region, as well as early hematopoiesis, by mediating attachment to stromal cells. Mutations in this gene are associated with fatal classic Kaposi sarcoma, immunodeficiency due to defects in store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) in fibroblasts, ectodermal dysplasia and tubular aggregate myopathy. This gene is oriented in a head-to-tail configuration with the ribonucleotide reductase 1 gene (RRM1), with the 3' end of this gene situated 1.6 kb from the 5' end of the RRM1 gene.
Activation-Induced deoxycytidine Deaminase (AID)
I asked about Activation-Induced deoxycytidine Deaminase (AID), involved in Immunoglobulin diversification by initiating Somatic Hypermutation (SHM) and Class-Switch Recombination (CSR) in B-cells?
Synonyms are enough to drive you crazy when trying to probe this topic as this summary from CTD shows.
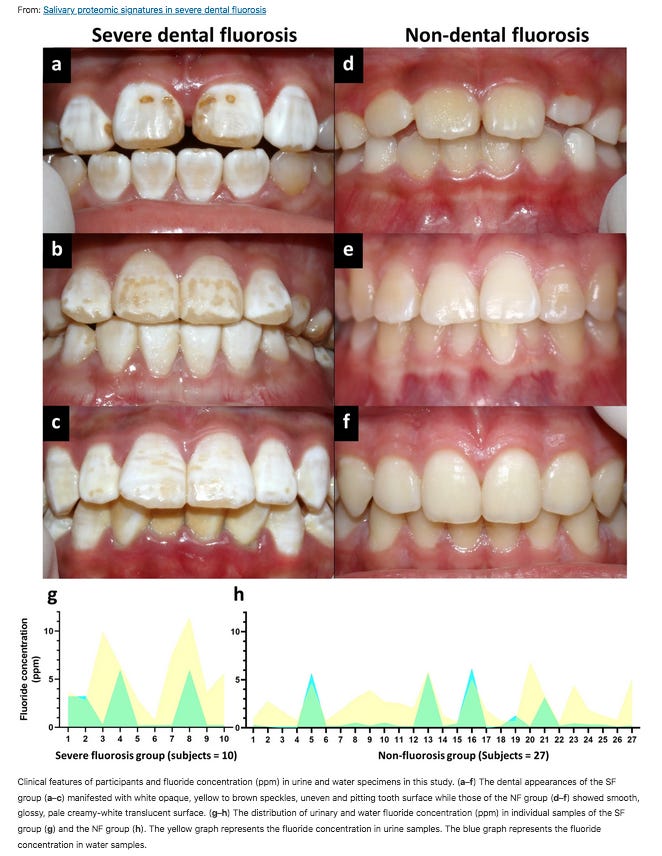
Genes involved in Dental Fluorosis
A recent paper from researchers in Thailand examined Saliva and found a variety of proteins with altered expression correlated Dental Severe Fluorosis with Fluoride in drinking water and urine.4
Five proteins significantly upregulated in the Severe Fluorosis group - LDHA, UBA1, S100A9, H4C3, and LCP1 were connected to an ion channel, CFTR (CF transmembrane conductance regulator) that is thought to “play a predominant role in severe fluorosis and highlighted the depletion of immune-related salivary proteins, suggesting compromised immune defense in severe fluorosis.”
Friends are invited to tell us what they find
Clearly the literature is enormous, so steering a pathway to understanding is a collective effort and each person who looks will see a different highlight.
Humans, thankfully, are smarter than “Artificial Intelligence”.
My friend Andreas Schuld kindly directed me to his page5 where he assembled literature relating to Covid19 replication requiring activation of the NF-κB pathway.
Has your Fluoridated Water Supplier told you ?
Hoping that some of the Genes affected by Fluoride ring a bell with readers who are delving into the epigenetic toxic effects of Covid19 Jabs.
You will recall that many of these same genes are affected by Endotoxin.
Geoff Pain 4 Feb 2020. https://www.researchgate.net/post/Could_areas_of_high_Fluoride_ingestion_be_more_susceptible_to_Coronavirus_outbreaks
Geoff Pain. 20 July 2021. https://www.researchgate.net/post/Fluoride_Inhibition_of_Activation-induced_deoxycytidine_deaminase_possible_interference_with_Somatic_Hypermutation_required_for_Immunity_to_COVID-19
Edward J Steele, Joseph F Williamson, Susan Lester, Brent J Stewart, John A Millman, Pat Carnegie, Robyn A Lindley, Geoff N Pain and Roger L Dawkins. 2011. Genesis of ancestral haplotypes: RNA modifications and RT-mediated polymorphisms. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0198885910005689
Patcharaporn Gavila, Penpitcha Ajrithirong, Supoj Chumnanprai, Nuttiya Kalpongnukul, Trairak Pisitkun, Soranun Chantarangsu, Kanokwan Sriwattanapong, Junji Tagami and Thantrira Porntaveetus. 2024. Salivary proteomic signatures in severe dental fluorosis. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-69409-0
https://poisonfluoride.com/phpBB3/viewtopic.php?f=66&t=1888