Endotoxin Contamination of Asparaginase Jabs
Leukemia victims suffered from Endotoxin in jabs made from E. coli, so drug companies changed the bacteria used to Erwinia Chrysanthemi
Covid19 mRNA jabs are contaminated with undisclosed amounts of Endotoxin and I have written extensively how that can account for a host of the Adverse Reactions after the jabs, especially those recorded within Minutes to Days, before the body can make any antibodies to the Spike Protein coded by the Synthetic mRNA.
It helps to look at the Adverse Reactions to Endotoxin contamination in another class of jabs, so here I look at Asparaginase, also known as Crisantaspase, or Colaspase used as a Leukemia treatment.1
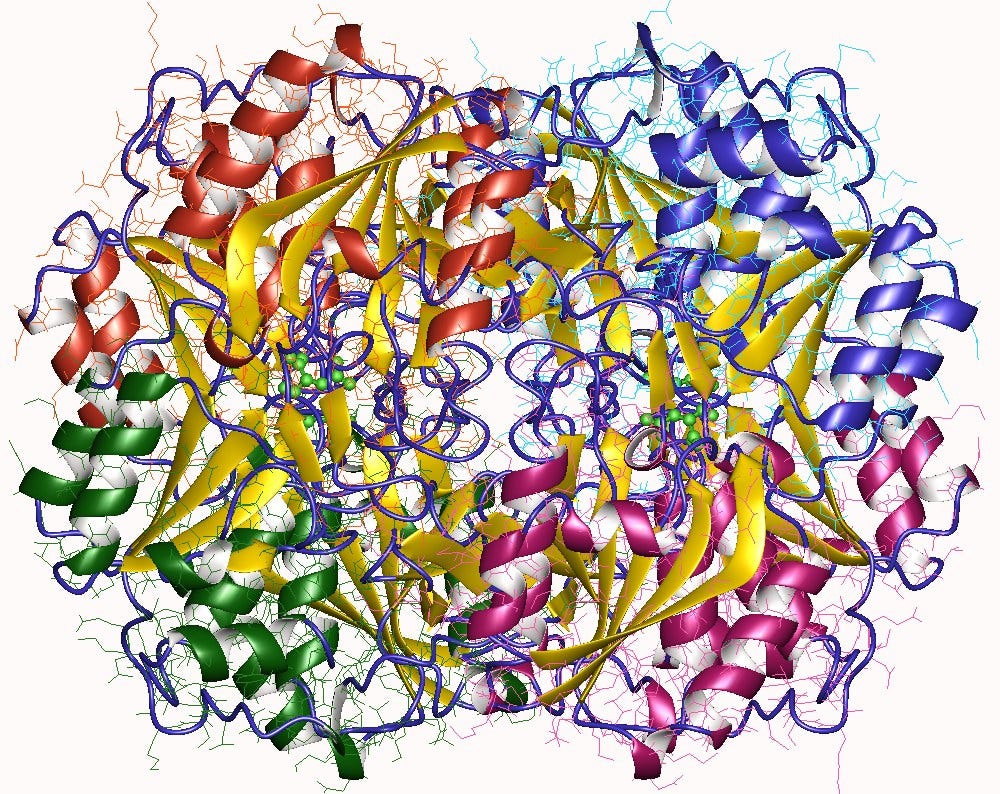
The crystal structure of this E. coli enzyme was determined in 1993.2
It exists primarily as a tetramer with molecular mass >280 kDa.
Endotoxin was identified as a major problem in Asparaginase extracted from different bacteria because there are so many bonding sites for the small Lipid A Endotoxin.3
The abstract is available:
A retrospective study was undertaken comparing the frequency and severity of anaphylactic reactions to E. coli-derived and Erwinia-derived asparaginase given intravenously on a weekly dosage schedule. Both drugs were found to produce life-threatening hypersensivity reactions with the chance of reaction per dose administered being almost identical--8% for each dose administered. Eleven of 31 patients (35%) experienced anaphylactic reactions, 9/27 (33%) with E. coli and 3/10 (30%) with Erwinia asparaginase, with one patient suffering anaphylaxis to both preparations. A marked increase in the percentage of patients having reactions occurred after the fourth dose of either preparation, with the incidence per dose increasing from 3.3% with the first dose to 32% on the fifth and subsequent doses. Rationale for an antibody-mediated allergic reaction is presented to explain the data.
Toxic symptoms of Endotoxin Contaminated Asparaginase
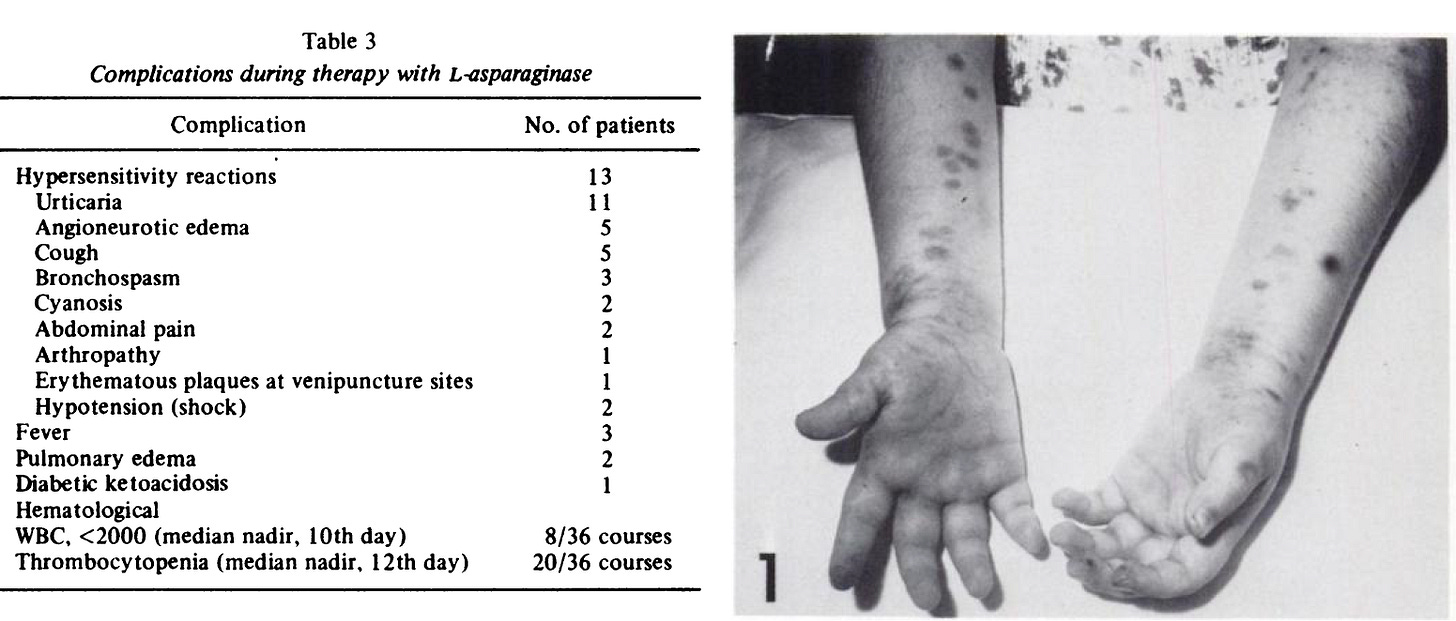
In 1970 Leukemia patients4 suffered from contaminated Asparaginase:
Fever, nausea and vomiting, weight loss, somnolence, lethargy, confusion, hypolipidemia, hyperlipidemia, hypoproteinemia, abnormal liver function tests, fatty metamorphosis of the liver, pancreatitis (in rare instances), azotemia, granulocytopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, and hypersensitivity reactions.
Patients were given high contamination injections, in the range of 1/100th to 1/1000th the Lethal Dose for Humans, as guessed by testing in Rabbits!
Endotoxin contaminated Asparaginase does this to Leukemia patients. Considered tolerable because all were terminal without trying something. Note the similarity to Pfizer Process 2 Harms.5
These experiments revealed that Asparaginase is toxic itself, adding complications to estimation of the impact of the Endotoxin.6
L-asparaginase caused a greater incidence of tremors, muscle fasciculations and ultimate convulsions than endotoxin. Endotoxin toxicity was observed within 24 h, whereas L-asparaginase intoxication developed after 24 h. The blood pressure in animals displaying severe L--asparaginase toxicity was similar to that monitored in the control animals, whereas severe hypotension was found in endotoxin-intoxicated animals. L-asparaginase and endotoxin induced increases in blood glucose and urea nitrogen. The blood urea nitrogen levels returned to control levels by 72 h in surviving animals. Endotoxin also produced elevations in serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase and serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase levels. Endotoxin and L-asparaginase produced some histopathological changes in the lung, kidney, liver and spleen. The alterations in the liver and kidney appeared to be more severe after endotoxin treatment. Significant decreases in plasma levels of calcium and magnesium and an increase in plasma phosphorus levels were noted in L-asparaginase-intoxicated animals. These plasma ions were not altered by endotoxin treatment.
In 1972, more measurement7 of Endotoxin in commercial samples of Asparaginase was performed because it had been linked to Renal Failure, abnormal Clotting Factors and Edema. In 1975 Central Nervous System toxicity and allergic reactions were observed at high- and low-dose levels.8
In 1976 Endotoxin in Asparaginase was measured up to 4 ng/ml (4,000 pg.ml).9
In Humans immediate hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis with intravenous injection has been observed with delayed allergic reactions occurring hours after intramuscular Asparaginase administration.10
Recently Endotoxin contamination associated with severe adverse reactions has been measured up to 41 EU/ml in a number of commercial Asparaginase products available in India.11
Affinity Chromatography has been used to reduce Endotoxin in Asparaginase but the profit motive in BigPharma prevents upscale using this technique.12
E Coli Cell-free Asparaginase
Because the Endotoxin contamination is intractable, Endotoxin-Free E. coli-Based Cell-Free Protein Synthesis of Asparaginase has been demonstrated using genetically engineered, endotoxin-free ClearColi cells.13
Questions Arising
Do the mRNA Covid19 jabs contain toxic Asparaginase as well as Endotoxin?
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asparaginase
Swain AL, et al. 1993. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase, an enzyme used in cancer therapy. https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.90.4.1474
Dellinger CT and Miale TD. 1976. Comparison of anaphylactic reactions to asparaginase derived from Escherichia coli and from Erwinia cultures. Cancer. 1976 Oct;38(4):1843-6.
Oettgen HF, et al. 1970. Toxicity of E. coli L-asparaginase in man. https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/1097-0142(197002)25:2%3C253::aid-cncr2820250204%3E3.0.co;2-u
Jaffe N et al. 1971. L-Asparaginase in the Treatment of Neoplastic Diseases in Children. Cancer Research 31:942-949
Herman EH, et al. 1973. A Comparison of Some Pharmacological Effects of Escherichia coli (E. coli) L-Asparaginase and E. coli Endotoxin in Rabbits. https://karger.com/pha/article-abstract/9/2/85/271928/A-Comparison-of-Some-Pharmacological-Effects-of
Loos M, et al. 1972. Detection of Endotoxin in Commercial l-Asparaginase Preparations by Complement Fixation and Separation by Chromatography. https://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article/32/11/2292/478607/Detection-of-Endotoxin-in-Commercial-l
Wilson WL, et al, 1975. Phase I Study of L-Asparaginase (NSC 109229). https://karger.com/ocl/article-abstract/32/3-4/109/234363/Phase-I-Study-of-L-Asparaginase-NSC-109229.
Siegel SE et al. 1976. Detection of bacterial endotoxin in antitumor agents. Cancer Treatment Reports. 1976 Jan;60(1):9-15.
Spiegel RJ et al. 1980. Delayed allergic reactions following intramuscular L-asparaginase. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mpo.2950080204
Sidhu J, et al. 2021. Unsatisfactory quality of E. coli asparaginase biogenerics in India: Implications for clinical outcomes in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/pbc.29046
Lee S_M, et al. 1989. L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora An improved recovery and purification process using affinity chromatography. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02922693
Wilding KM et al. 2018. Endotoxin-Free E. coli-Based Cell-Free Protein Synthesis: Pre-Expression Endotoxin Removal Approaches for on-Demand Cancer Therapeutic Production. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/biot.201800271



I read this and thought of you. Endotoxin in cultured meat.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.04.21.537778v1
https://dailysceptic.org/2023/06/18/lab-grown-meat-suffers-significant-setback-with-shocking-new-scientific-findings/