CD4/CD8 Ratio is altered by Endotoxin in Covid19 Jabs
Decreasing your CD4/CD8 ratio is a very bad idea
I discussed the CD4/CD8 ratio in an earlier post this year.
Gay Men, Pregnant Women and Foetuses - What do they have in common?
I thank Walter M Chesnut for bringing this journal article graphical abstract by Shin Jie Yong to my attention. I have shaved the top of the figure off for reasons which will become apparent.Geoff Pain PhD is a reader-supported publication. Please consider upgrading as a paid subscriber.
My good friend Chris Edwards1 in England has been intensively studying the impact of the Pfizer jabs on the Immune System and discovered that 2 jabs in trial subjects produced more activated CD8+ cells than CD4+ cells in jabbees than in a control group of people who had recovered from Covid19 infection. This exactly the opposite of what is required in a healthy immune system.
Here is data obtained from the TGA by FOI demand.2
The US FDA was fully aware of this in early December 2020.3
Note that the CD8+ cells expressing the nasty IFN-γ molecules were more abundant than the activated CD4+ cells 29 days after the insult.
Chris pointed to a 2022 paper by Grimaldi and coworkers4 who found a clear warning sign that the CD4/CD8 ratio was upset by jabbing.
we observed circulating leukocyte T cell response in healthy subjects, COVID-19 infected, and in healthy vaccinated subjects. We found a significant CD8+ T cells (p < 0.05) decrease and an augmented CD4+/CD8+ ratio (p < 0.05) in COVID-19 infected group compared with vaccinated subjects. In addition, healthy vaccinated subjects have a significant increased expression of CD8+ T cells, and a reduction of CD4+/CD8+ ratio with respect to subjects previously COVID-19 infected.
This is of course a worry with regard to Autoimmune Diseases caused by the jabs.
Another very good friend helped me out, directing me to a nice paper by Stebegg and coworkers5 that helps explain what happens when the Lymph Nodes are targeted by the jabs. I have abbreviated the quoted material so the interested reader should refer to the full free text. The purpose is to identify key molecules and processes that can be disrupted by jabbing.
In the T cell zone, fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) orchestrate the migration, localization and survival of DCs, T cells and B cells by producing CCL19, CCL21, and CXCL12. The CCL19/21 produced by FRCs enables localization of both CD4+ T cells and DCs to the T cell zone, via CCR7-mediated migration, bringing these rare cells together to facilitate T cell priming and activation. In the B cell follicles there are two types of stromal cells: follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) that produce CXCL13 and CXCL12-producing reticular cells (CRCs) which promote the localization of B cells during the germinal center response. FRCs at the boundary of the T cell zone and follicle produce B cell-activating factor (BAFF) to maintain the primary follicle structure. Antigen encounter by naïve B cells is facilitated by CXCR5-mediated migration toward the CXCL13-rich follicles. This localizes them close to the SubCapsular Sinus (SCS) where small soluble antigens are drained and can directly trigger B cell activation. Alternatively, antigens drained through the SCS can be captured by follicular FDCs which typically recognize antigen bound by antibody and/or complement, known as Immune Complexes (ICs). FDCs are able to retain antigen on their surface for prolonged periods of time, allowing B cells to scan the follicular FDC network for cognate antigen to trigger activation. The SCS facilitates the movement of lymph fluid and is lined by Marginal Reticular Cells (MRCs), which are FDC precursors and provide structural support. The distribution of these stromal cells in specific areas of the SLOs facilitates the continuous circulation and subsequent activation of lymphocytes that enter the LNs and Peyer's patches (PPs) through High Endothelial Venules (HEV). Activated CD4+ T cells begin to downregulate CCR7 and upregulate CXCR5 which allows them to move away from the CCL19/21-rich T cell zone and toward the interfollicular region. Simultaneously, activated B cells upregulate CCR7 while maintaining CXCR5 expression which allows them to move toward the edge of the follicle at the T:B interface. Both cell types upregulate Epstein-Barr virus-induced G protein coupled receptor 2 (EBI2). The final step for GC formation requires activated CD4+ T cells and B cells to migrate to the follicle from the T:B border as GC B cells and fully differentiated Tfh cells. Both CD4+ T cells and B cells downregulate CCR7 and EBI2 whilst stably expressing CXCR5.
During GC formation FDCs also become activated through TLR4 and B-cell derived LymphoToxin (LT) α1β2 signaling. The activation of FDCs also triggers an increase in their expression of antigen-capture molecules such as CD35, CD21, and FcγRII. This allows antigen-specific B cells to test their Ig receptors by capturing antigen from FDCs to subsequently internalize, process and present the antigen peptides to Tfh cells in order to receive critical survival signals. FDCs can also produce cytokines such as IL-6, and IL-15 that promote SHM and IgG production and support B cell proliferation, respectively. FDC production of FDC-M1 aids in the clearance of apoptotic GC B cells as FDC-M1 coats B cells, marking them for clearance by tangible-body macrophages. For Tfh cells to be retained in the GC they must express not only S1PR2, but also SLAM-associated protein (SAP), which promotes antigen-specific T-B adhesion. T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells are derived from Foxp3+ precursors. Tfr cell differentiation culminates in the expression of Bcl-6, the master transcriptional regulator for Tfr cell differentiation. Transcription factor Nuclear Factor of Activated T cells 2 (NFAT2, also known as NFATc1) is required for CXCR5 upregulation on Treg cells through binding to the Cxcr5 promoter. Tfr cell differentiation also requires an intricate network of many other molecules, such as Stromal Interaction Molecule 1 (STIM1) and STIM2, Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor (TNFR)-associated factor 3 (TRAF3), Signal Transducer and Activator 3 (STAT3), p85α-osteopontin, and members of the helix-loop-helix family (E and Id proteins).
CD8 Alpha- and CD8 Alpha+ cells
Reference 23 in Stebegg et al. takes us to the CD8 cell story by Shin and coworkers (2015).6 Here we learn Tfh cells induced by CD8α− are true B cell helpers, resulting in significantly increased humoral immune responses against various human pathogenic antigens.
They showed that, once again abbreviated, in the presence of Endotoxin Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) :
higher percentages and numbers of CXCR5+PD1+, CXCR5+Bcl6+, and CXCR5+IL-21+ Tfh cells were induced by CD8α− DCs in the lymph nodes and spleen compared with those induced by CD8α+ DCs. CD4+ T cells induced by CD8α− DCs in the presence of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) expressed higher levels of CXCR5 and ICOS. CD8α− DCs expressed higher levels of ICOSL with both poly(I:C) (a synthetic DNA analog) and LPS. CD8α+ DCs expressed higher levels of PDL1 and PDL2 which are known to negatively regulate Tfh-dependent humoral immune responses.
Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF1α)
In 2017 Avendaño-Ortiz and coworkers7 showed that the transcription factor Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF1α) is translocated into the nucleus and drives PD-L1 expression during Endotoxin Tolerance (ET) in Human Monocytes. They found an inverse correlation between the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation (APACHE) II score and TNFα production which allowed them to classify patients with Sepsis into 3 subgroups. The APACHE II, quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (qSOFA) scale, Glasgow Coma scale, Heart rate, Oxygen Saturation, Lactate, and outcome showed significant differences between subgroups, and a link with ET status.
Programmed Cell Death
Shin et al. (2015) lead us to Hams et al (2011).8 They found that the Programmed Death Ligand 1 (B7-H1/PD-1) pathway is one mechanism behind CD8+ T cell exhaustion (tolerance induction) that results in ineffective T cell viral immunity during chronic viral infections, such as HIV. PD-1 expression on CD4+ T cells acts to limit activation-induced CD4+ T cell expansion and function, but plays no role in the induction of peptide-induced tolerance. Hams reminds us with reference to Dong and coworkers (2004)9 that “the percentage of Interferon gamma (IFN-γ)–producing Th1 cells was higher in B7-H1−/− mice compared with Wild Type (WT) mice in response to S. mansoni infection, consistent with observations shown by another group”.
This history brings us to a recent paper that provides further information on the role of CD8+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) cells induced by Endotoxin by Morita and coworkers.10 They studied induced Endotoxic Shock in young (8–12 wk old) and aged (18–20 months old) mice. “The adoptive transfer of CD8+ Tregs into LPS-treated young mice improved the survival rate of LPS-induced endotoxic shock”. The number of CD8+ Tregs in LPS-treated young mice increased through the induction of IL-15 produced by CD11c+ cells. In contrast, Endotoxin aged mice showed a reduced induction of CD8+ Tregs owing to the limited production of IL-15.
Joining the Dots
Endotoxin > transcription factor Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF1α) translocated into the nucleus and drives increased PD-L1/programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) > reduced T follicular helper (TFH) cells which are needed for humoral immune responses against various human pathogenic antigens.
Clearly the MHRA, FDA, EMA and TGA knew before the jabs were rolled out that they mucked up the immune system. The differences between young and old and tolerance disruption will be explored further and references added when my friends here and on Twitter weigh in with their expertise.
https://twitter.com/ChrisEd16512812
Pfizer Australia. Nonclinical Evaluation of BNT162b2 [mRNA] COVID-19 vaccine (COMIRNATY). Submission No. PM-2020-05461-1-2 obtained as FOI-2389 part 6 from Therapeutic Goods Administration. https://www.tga.gov.au/foi-disclosure-log
Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee December 10, 2020 Meeting Briefing Document- Sponsor, CBER, Biologics. https://www.fda.gov/media/144246/download
Grimaldi V, et al. 2022. Evaluation of circulating leucocyte populations both in subjects with previous SARS-COV-2 infection and in healthy subjects after vaccination. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022175922000175
Stebegg M, et al. 2018. Regulation of the Germinal Center Response. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6209676/
Shin C, et al. CD8α− Dendritic Cells Induce Antigen-Specific T Follicular Helper Cells Generating Efficient Humoral Immune Responses. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211124715005781
Avendaño-Ortiz J, et al. PD-L1 Overexpression During Endotoxin Tolerance Impairs the Adaptive Immune Response in Septic Patients via HIF1α. https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/217/3/393/4056038
Hams E, et al. 2011. Blockade of B7-H1 (programmed death ligand 1) enhances humoral immunity by positively regulating the generation of T follicular helper cells. https://journals.aai.org/jimmunol/article/186/10/5648/84080/Blockade-of-B7-H1-Programmed-Death-Ligand-1
Dong H, et al. 2004. B7-H1 determines accumulation and deletion of intrahepatic CD8+ T lymphocytes. https://www.cell.com/immunity/fulltext/S1074-7613(04)00050-0
Morita N, et al. 2023. CD8+ Regulatory T Cells Induced by Lipopolysaccharide Improve Mouse Endotoxin Shock. https://journals.aai.org/immunohorizons/article/7/5/353/263818/CD8-Regulatory-T-Cells-Induced-by





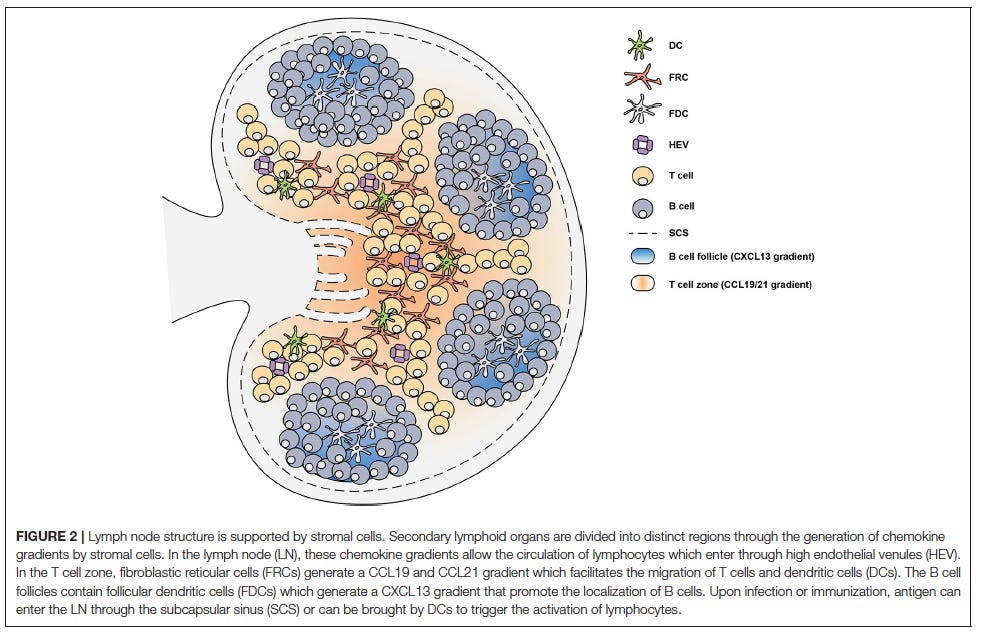


I don’t understand much of this apart from the conclusion. The lesson we should learn is that our immune system is a highly tuned system that we mess with at our peril. Look after your immune health with good food, fresh air, regular sleep, a daily walk, sunshine and vitamin D supplement in the winter months.